Page 211 - DMGT551_RETAIL_BUSINESS_ENVIRONMENT
P. 211
Retail Business Environment
Notes
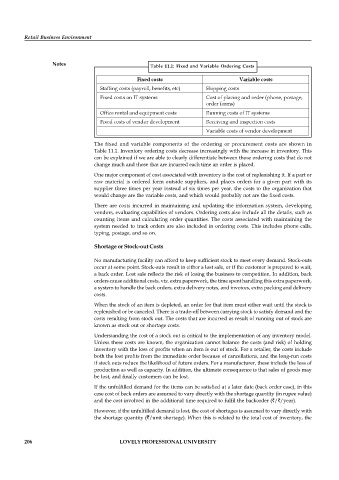
Table 11.1: Fixed and Variable Ordering Costs
Fixed costs Variable costs
Staffing costs (payroll, benefits, etc) Shipping costs
Fixed costs on IT systems Cost of placing and order (phone, postage,
order forms)
Office rental and equipment costs Running costs of IT systems
Fixed costs of vendor development Receiving and inspection costs
Variable costs of vendor development
The fixed and variable components of the ordering or procurement costs are shown in
Table 11.1. Inventory ordering costs decrease increasingly with the increase in inventory. This
can be explained if we are able to clearly differentiate between those ordering costs that do not
change much and those that are incurred each time an order is placed.
One major component of cost associated with inventory is the cost of replenishing it. If a part or
raw material is ordered form outside suppliers, and places orders for a given part with its
supplier three times per year instead of six times per year, the costs to the organization that
would change are the variable costs, and which would probably not are the fixed costs.
There are costs incurred in maintaining and updating the information system, developing
vendors, evaluating capabilities of vendors. Ordering costs also include all the details, such as
counting items and calculating order quantities. The costs associated with maintaining the
system needed to track orders are also included in ordering costs. This includes phone calls,
typing, postage, and so on.
Shortage or Stock-out Costs
No manufacturing facility can afford to keep sufficient stock to meet every demand. Stock-outs
occur at some point. Stock-outs result in either a lost sale, or if the customer is prepared to wait,
a back order. Lost sale reflects the risk of losing the business to competition. In addition, back
orders cause additional costs, viz. extra paperwork, the time spent handling this extra paperwork,
a system to handle the back orders, extra delivery notes, and invoices, extra packing and delivery
costs.
When the stock of an item is depleted, an order for that item must either wait until the stock is
replenished or be canceled. There is a trade-off between carrying stock to satisfy demand and the
costs resulting from stock out. The costs that are incurred as result of running out of stock are
known as stock out or shortage costs.
Understanding the cost of a stock out is critical to the implementation of any inventory model.
Unless these costs are known, the organization cannot balance the costs (and risk) of holding
inventory with the loss of profits when an item is out of stock. For a retailer, the costs include
both the lost profits from the immediate order because of cancellations, and the long-run costs
if stock outs reduce the likelihood of future orders. For a manufacturer, these include the loss of
production as well as capacity. In addition, the ultimate consequence is that sales of goods may
be lost, and finally customers can be lost.
If the unfulfilled demand for the items can be satisfied at a later date (back order case), in this
case cost of back orders are assumed to vary directly with the shortage quantity (in rupee value)
and the cost involved in the additional time required to fulfil the backorder (`/`/year).
However, if the unfulfilled demand is lost, the cost of shortages is assumed to vary directly with
the shortage quantity (`/unit shortage). When this is related to the total cost of inventory, the
206 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY