Page 114 - DCOM303_DMGT504_OPERATION_RESEARCH
P. 114
Unit 5: Transportation Problem
Notes
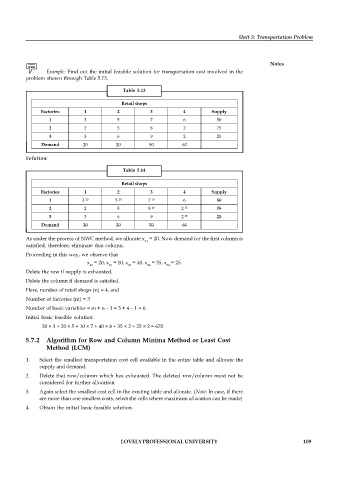
Example: Find out the initial feasible solution for transportation cost involved in the
problem shown through Table 5.13.
Table 5.13
Retail shops
Factories 1 2 3 4 Supply
1 3 5 7 6 50
2 2 5 8 2 75
3 3 6 9 2 25
Demand 20 20 50 60
Solution:
Table 5.14
Retail shops
Factories 1 2 3 4 Supply
1 3 5 7 6 50
20
10
20
2 2 5 8 2 75
35
40
25
3 3 6 9 2 25
Demand 20 20 50 60
As under the process of NWC method, we allocate x = 20. Now demand for the first column is
11
satisfied, therefore, eliminate that column.
Proceeding in this way, we observe that
x = 20, x = 10, x = 40, x = 35, x = 25.
12 13 23 24 34
Delete the row if supply is exhausted.
Delete the column if demand is satisfied.
Here, number of retail shops (n) = 4, and
Number of factories (m) = 3
Number of basic variables = m + n – 1 = 3 + 4 – 1 = 6.
Initial basic feasible solution:
20 × 3 + 20 × 5 + 10 × 7 + 40 × 8 + 35 × 2 + 25 × 2 = 670
5.7.2 Algorithm for Row and Column Minima Method or Least Cost
Method (LCM)
1. Select the smallest transportation cost cell available in the entire table and allocate the
supply and demand.
2. Delete that row/column which has exhausted. The deleted row/column must not be
considered for further allocation.
3. Again select the smallest cost cell in the existing table and allocate. (Note: In case, if there
are more than one smallest costs, select the cells where maximum allocation can be made)
4. Obtain the initial basic feasible solution.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 109