Page 296 - DCOM303_DMGT504_OPERATION_RESEARCH
P. 296
Unit 14: Decision-making
Notes
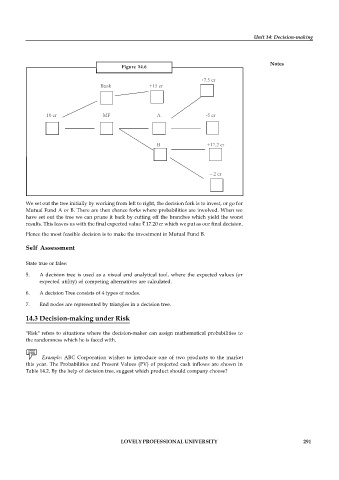
Figure 14.6
+7.5 cr
Bank +15 cr
10 cr ` MF A -5 cr
B +17.2 cr
– 2 cr
We set out the tree initially by working from left to right, the decision fork is to invest, or go for
Mutual Fund A or B. There are then chance forks where probabilities are involved. When we
have set out the tree we can prune it back by cutting off the branches which yield the worst
results. This leaves us with the final expected value ` 17.20 cr which we put as our final decision.
Hence the most feasible decision is to make the investment in Mutual Fund B.
Self Assessment
State true or false:
5. A decision tree is used as a visual and analytical tool, where the expected values (or
expected utility) of competing alternatives are calculated.
6. A decision Tree consists of 4 types of nodes.
7. End nodes are represented by triangles in a decision tree.
14.3 Decision-making under Risk
"Risk" refers to situations where the decision-maker can assign mathematical probabilities to
the randomness which he is faced with.
Example: ABC Corporation wishes to introduce one of two products to the market
this year. The Probabilities and Present Values (PV) of projected cash inflows are shown in
Table 14.2. By the help of decision tree, suggest which product should company choose?
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 291