Page 125 - DMGT505_MANAGEMENT_INFORMATION_SYSTEM
P. 125
Management Information Systems
Notes Whenever an upper-layer protocol delivers data segments whose sizes exceed the limit allowed
by the underlying network, IP breaks the data into smaller pieces that are manageable within
the allowed limit. The small datagrams are then sent to the target host, which reassembles them
for subsequent delivery to an upper-layer protocol.
Data fragments, however, takes the same route but there is instances when they may adopt
alternate route too. Fragments traversing different routes may reach their destination out of the
order in which they were sent. To allow for recovery from such a behavior, IP employs the
fragmentation-offset field in its header. The fragmentation-offset field includes sequencing
information that the remote IP host uses to recover the sequence in which the datagrams were
sent. The fragmentation-offset field also contains information for detecting missing fragments,
which is used by IP. Data is passed to the protocol described in the protocol field only when all
related fragments are duly received and reordered, it is known as data reassembly.
Fragments belonging to two or more independent large data can be differentiated by IP using
identification field. Fragments of the same datagram are uniquely assigned in the identification
field. The receiving end uses this number to recover the IP fragments to their respective datagrams.
A host that creates a datagram can set a bit in the flag field to specify the fragmentation. This bit
is set to 1 in all fragments belonging to a datagram except for the final fragment. This ensures
that all fragments of a datagram are received.
1. Echo request/Echo reply: These two ICMP messages are exchanged between ICMP software
on any two hosts in a bid to check connectivity between them. The ping command is an
example of a diagnostic command commonly used by network users to check for the
reachability of a certain host. On invoking this command, ICMP echo request message is
sent to the target host. The target host responds with an echo as proof of reachability. It
should however be operational and connected to the network. In other words, the reply
carries the same data as the request.
2. Address Mask Request/Reply: A host broadcasts an address mask request when it boots,
and routers that receive the request send an address mask reply that contains the correct
32-bit subnet mask being used on the network.
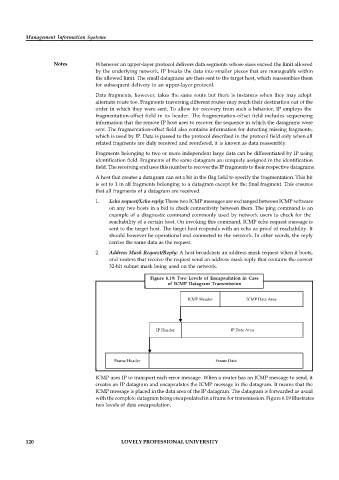
Figure 6.19: Two Levels of Encapsulation in Case
of ICMP Datagram Transmission
ICMP Header ICMP Data Area
IP Header IP Data Area
Frame Header Frame Data
ICMP uses IP to transport each error message. When a router has an ICMP message to send, it
creates an IP datagram and encapsulates the ICMP message in the datagram. It means that the
ICMP message is placed in the data area of the IP datagram. The datagram is forwarded as usual
with the complete datagram being encapsulated in a frame for transmission. Figure 6.19 illustrates
two levels of data encapsulation.
120 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY