Page 126 - DMGT505_MANAGEMENT_INFORMATION_SYSTEM
P. 126
Unit 6: Business Networks and Telecommunications
IGMP Notes
The computer networks offer a collaborative and best effort to reliable deliver by forwarding a
data packet from one node to another so that it could reach to destination in the best possible
ways. The nodes receiving multicast messages inform their immediately neighboring routers.
In the IGMP, each node belongs to one or more multicast groups to receive multicast data
packets. Hence, Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) enables nodes to exchange
information with their local routers and provides a mechanism through which a host can join or
leave a multicast group at any time (dynamic membership). The IGMP used by IP hosts and
adjacent multicast routers aims to manage the membership of IP multicast groups.
RFC 1112 defines 3 versions of IGMP. Similar to ICMP, IGMP is also an integral part of the
Internet Protocol (IP) and operates above the network layer. It is the job of the routers to use
IGMP periodically to check if the known group members are active or not. A host group is the
collection of hosts interested in traffic for a particular multicast address. If there is more than one
multicast router on a subnetwork, one of them is selected as the “querier” to keep track of the
membership state of the multicast groups having active members on its subnetwork. When
router receives a multicast packet, it checks whether there is at least one member of that group
on its subnetwork to forward the message to that subnetwork, otherwise, router discards the
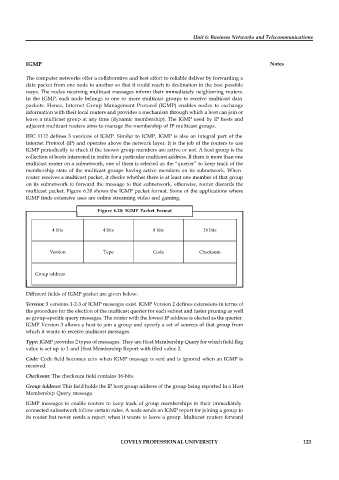
multicast packet. Figure 6.20 shows the IGMP packet format. Some of the applications where
IGMP finds extensive uses are online streaming video and gaming.
Figure 6.20: IGMP Packet Format
4 bits 4 bits 8 bits 16 bits
Version Type Code Checksum
Group address
Different fields of IGMP packet are given below:
Version: 3 versions 1-2-3 of IGMP messages exist. IGMP Version 2 defines extensions in terms of
the procedure for the election of the multicast querier for each subnet and faster pruning as well
as group-specific query messages. The router with the lowest IP address is elected as the querier.
IGMP Version 3 allows a host to join a group and specify a set of sources of that group from
which it wants to receive multicast messages.
Type: IGMP provides 2 types of messages. They are Host Membership Query for which field flag
value is set up to 1 and Host Membership Report with filed value 2.
Code: Code field becomes zero when IGMP message is sent and is ignored when an IGMP is
received.
Checksum: The checksum field contains 16-bits.
Group Address: This field holds the IP host group address of the group being reported In a Host
Membership Query message.
IGMP messages to enable routers to keep track of group memberships in their immediately
connected subnetwork follow certain rules. A node sends an IGMP report for joining a group to
its router but never sends a report when it wants to leave a group. Multicast routers forward
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 121