Page 183 - DMGT505_MANAGEMENT_INFORMATION_SYSTEM
P. 183
Management Information Systems
Notes 9.5.1 Future of M-commerce
The futures of mobile commerce are:
1. Ubiquity: It means that the user can avail of services and carry out transactions largely
independent of his current geographic location.
2. Immediacy: It provides real-time availability of services.
3. Localization: Location based services such as GPS, allow companies to offer goods and
services to the user specific to his current location.
4. Instant connectivity: This feature brings convenience to the user, due to introduction of
services like GPRS which keeps users always in touch and connected.
5. Simple authentication: Mobile telecommunication devices function with an electronic
chip called SIM, which is easily identifiable. This in combination with an individual
Personal Identification Number (PIN) makes the authentication process simple.
9.5.2 Specific Advantages of Mobile Commerce
The specific advantages of mobile commerce are:
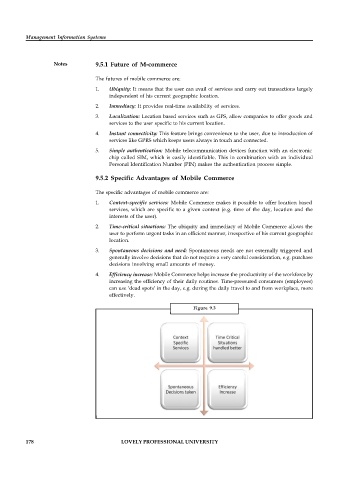
1. Context-specific services: Mobile Commerce makes it possible to offer location based
services, which are specific to a given context (e.g. time of the day, location and the
interests of the user).
2. Time-critical situations: The ubiquity and immediacy of Mobile Commerce allows the
user to perform urgent tasks in an efficient manner, irrespective of his current geographic
location.
3. Spontaneous decisions and need: Spontaneous needs are not externally triggered and
generally involve decisions that do not require a very careful consideration, e.g. purchase
decisions involving small amounts of money.
4. Efficiency increase: Mobile Commerce helps increase the productivity of the workforce by
increasing the efficiency of their daily routines. Time-pressured consumers (employees)
can use ‘dead spots’ in the day, e.g. during the daily travel to and from workplace, more
effectively.
Figure 9.3
178 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY