Page 10 - DMGT513_DERIVATIVES_AND_RISK_MANAGEMENT
P. 10
Unit 1: Introduction to Derivatives
contracts. Swaps generally are traded OTC through swap dealers, which generally consist Notes
of large financial institution, or other large brokerage houses. There is a recent trend for
swap dealers to mark to market the swap to reduce the risk of counterparty default. The
two commonly used swaps are:
(a) Interest rate swaps: These entail swapping only the interest related cash flows between
the parties in the same currency.
Example: Suppose Party A holds a 10-year 10,000 home loan that has a fixed interest
rate of 7 %, and Party B holds a 10-year 10,000 home loan that has an adjustable interest rate that
will change over the "life" of the mortgage. If Party A and Party B were to exchange interest rate
payments on their otherwise identical mortgages, they would have engaged in an interest rate
swap.
(b) Currency swaps: These entail swapping both principal and interest between the parties,
with the cash flows in one direction being in a different currency than those in the
opposite direction. Swaps may involve cross-currency payments (U.S. Dollars vs.
Mexican Pesos) and crossmarket payments, e.g., U.S. short-term rates vs. U.K. short-
term rates.
1.2.2 Other Types of Financial Derivatives
1. Warrants: Options generally have lives of up to one year, the majority of options traded
on options exchanges having a maximum maturity of nine months. Longer-dated options
are called warrants and are generally traded over-the-counter.
2. LEAPS: The acronym LEAPS means Long-term Equity Anticipation Securities. These are
options having a maturity of up to three years
3. Baskets: Basket options are options on portfolios of underlying assets. The underlying
asset is usually a moving average of a basket of assets. Equity index options are a form of
basket options.
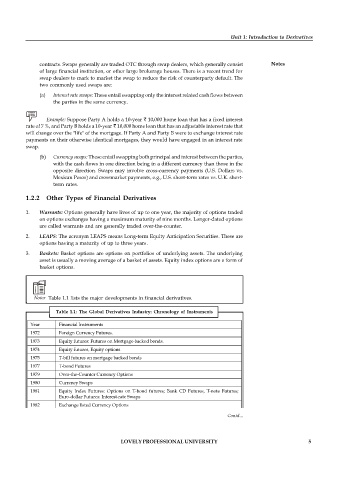
Notes Table 1.1 lists the major developments in financial derivatives.
Table 1.1: The Global Derivatives Industry: Chronology of Instruments
Year Financial Instruments
1972 Foreign Currency Futures.
1973 Equity futures: Futures on Mortgage-backed bonds.
1974 Equity futures, Equity options
1975 T-bill futures on mortgage backed bonds
1977 T-bond Futures
1979 Over-the-Counter Currency Options
1980 Currency Swaps
1981 Equity Index Futures: Options on T-bond futures; Bank CD Futures, T-note Futures;
Euro-dollar Futures: Interest-rate Swaps
1982 Exchange listed Currency Options
1983 Interest-rate Caps and Floor; Options on T-note, Futures; Currency Futures: Equity
Contd...
Index Futures
1985 Euro Dollar Options; SwapOptions; Futures on US Dollar & Municipal
Bond Indices
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY
1987 Average Options, Commodity Swaps, Bond Futures, Compound Options, OTC 5
Compound Options, OTC Average Options
1989 Three-month Euro-DM Futures Captions ECU ;Interest-rate Futures on Interest rate
Swaps
1990 Equity Index Swaps
1991 Portfolio Swaps
1992 Differential Swaps
1993 Captions; Exchange listed FLEX Options
1994 Credit Default Options
1995 Credit Derivatives
1996-98 Exotic Derivatives
2003-04 Energy Derivatives, Weather Derivatives