Page 11 - DMGT513_DERIVATIVES_AND_RISK_MANAGEMENT
P. 11
Derivatives & Risk Management
Notes
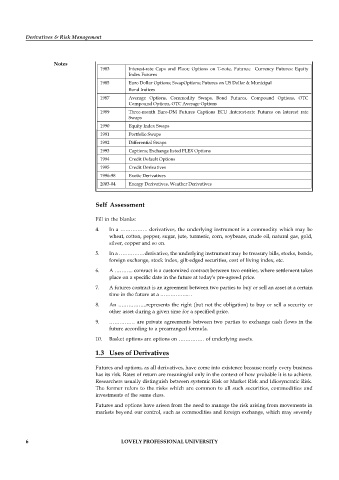
1983 Interest-rate Caps and Floor; Options on T-note, Futures; Currency Futures: Equity
Index Futures
1985 Euro Dollar Options; SwapOptions; Futures on US Dollar & Municipal
Bond Indices
1987 Average Options, Commodity Swaps, Bond Futures, Compound Options, OTC
Compound Options, OTC Average Options
1989 Three-month Euro-DM Futures Captions ECU ;Interest-rate Futures on Interest rate
Swaps
1990 Equity Index Swaps
1991 Portfolio Swaps
1992 Differential Swaps
1993 Captions; Exchange listed FLEX Options
1994 Credit Default Options
1995 Credit Derivatives
1996-98 Exotic Derivatives
2003-04 Energy Derivatives, Weather Derivatives
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
4. In a ……………. derivatives, the underlying instrument is a commodity which may be
wheat, cotton, pepper, sugar, jute, turmeric, corn, soybeans, crude oil, natural gas, gold,
silver, copper and so on.
5. In a ……………derivative, the underlying instrument may be treasury bills, stocks, bonds,
foreign exchange, stock index, gilt-edged securities, cost of living index, etc.
6. A ……….. contract is a customized contract between two entities, where settlement takes
place on a specific date in the future at today's pre-agreed price.
7. A futures contract is an agreement between two parties to buy or sell an asset at a certain
time in the future at a ……………... .
8. An ……………..represents the right (but not the obligation) to buy or sell a security or
other asset during a given time for a specified price.
9. …………… are private agreements between two parties to exchange cash flows in the
future according to a prearranged formula.
10. Basket options are options on …………… of underlying assets.
1.3 Uses of Derivatives
Futures and options, as all derivatives, have come into existence because nearly every business
has its risk. Rates of return are meaningful only in the context of how probable it is to achieve.
Researchers usually distinguish between systemic Risk or Market Risk and Idiosyncratic Risk.
The former refers to the risks which are common to all such securities, commodities and
investments of the same class.
Futures and options have arisen from the need to manage the risk arising from movements in
markets beyond our control, such as commodities and foreign exchange, which may severely
6 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY