Page 8 - DMGT513_DERIVATIVES_AND_RISK_MANAGEMENT
P. 8
Unit 1: Introduction to Derivatives
Notes
Notes Derivatives vs Shares
The subtle, but crucial, difference is that while shares are assets, derivatives are usually
contracts (the major exception to this are warrants and convertible bonds, which are
similar to shares in that they are assets). Well, we can define financial assets (e.g. shares,
bonds) as: claims on another person or corporation; they will usually be fairly standardized
and governed by the property or securities laws in an appropriate country. On the other
hand, a contract is merely an agreement between two parties, where the contract details
may not be standardized. Possibly because it is thought that investors may be wary of the
woolly definition of derivatives, one frequently comes across references to "derivatives
securities" or "derivatives products''. These "securities" and "products" sound fairly solid,
tangible things. But in many cases there terms are rather inappropriately applied to what
are really contracts.
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
1. Derivatives are ………………. whose value/price is dependent on the behaviour of the
price of one or more basic underlying assets.
2. A derivative by itself does not constitute …………..... .
3. A ………… is merely an agreement between two parties.
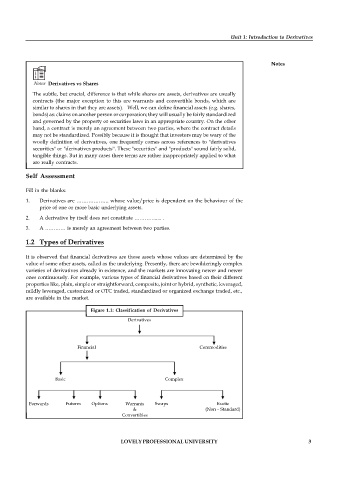
1.2 Types of Derivatives
It is observed that financial derivatives are those assets whose values are determined by the
value of some other assets, called as the underlying. Presently, there are bewilderingly complex
varieties of derivatives already in existence, and the markets are innovating newer and newer
ones continuously. For example, various types of financial derivatives based on their different
properties like, plain, simple or straightforward, composite, joint or hybrid, synthetic, leveraged,
mildly leveraged, customized or OTC traded, standardized or organized exchange traded, etc.,
are available in the market.
Figure 1.1: Classification of Derivatives
Derivatives
Financial Commodities
Basic Complex
Forwards Futures Options Warrants Swaps Exotic
& (Non – Standard)
Convertibles
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 3