Page 182 - DMGT513_DERIVATIVES_AND_RISK_MANAGEMENT
P. 182
Unit 13: Risk Management with Derivatives II
Notes
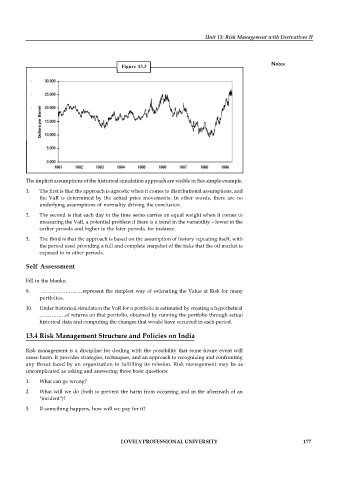
Figure 13.3
The implicit assumptions of the historical simulation approach are visible in this simple example.
1. The first is that the approach is agnostic when it comes to distributional assumptions, and
the VaR is determined by the actual price movements. In other words, there are no
underlying assumptions of normality driving the conclusion.
2. The second is that each day in the time series carries an equal weight when it comes to
measuring the VaR, a potential problem if there is a trend in the variability – lower in the
earlier periods and higher in the later periods, for instance.
3. The third is that the approach is based on the assumption of history repeating itself, with
the period used providing a full and complete snapshot of the risks that the oil market is
exposed to in other periods.
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
9. ……………………represent the simplest way of estimating the Value at Risk for many
portfolios.
10. Under historical simulation the VaR for a portfolio is estimated by creating a hypothetical
……………of returns on that portfolio, obtained by running the portfolio through actual
historical data and computing the changes that would have occurred in each period.
13.4 Risk Management Structure and Policies on India
Risk management is a discipline for dealing with the possibility that some future event will
cause harm. It provides strategies, techniques, and an approach to recognizing and confronting
any threat faced by an organization in fulfilling its mission. Risk management may be as
uncomplicated as asking and answering three basic questions:
1. What can go wrong?
2. What will we do (both to prevent the harm from occurring and in the aftermath of an
"incident")?
3. If something happens, how will we pay for it?
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 177