Page 171 - DMGT514_MANAGEMENT_CONTROL_SYSTEMS
P. 171
Management Control Systems
Notes 8.1 Variance Analysis for Control Actions
Since a budget is an instrument of control, it is necessary to compare the actual results with the
budgeted results. A variance occurs when actual costs differ from standard costs. The term
variance analysis refers to the systematic evaluation of variances in an attempt to provide
managers with useful information for measuring efficiency and improving performance.
If actual cost is less than the standard cost, the variance is favourable. If actual cost is more than
the standard cost, the variance is unfavourable. A favourable variance indicates efficiency and
an unfavourable variance indicates inefficiency.
Did u know? Variances occur due to three reasons. A managerial decision to respond to
some new developments which were not initially anticipated, uncontrollable exogenous
factors, and controllable factors that needs to be investigated.
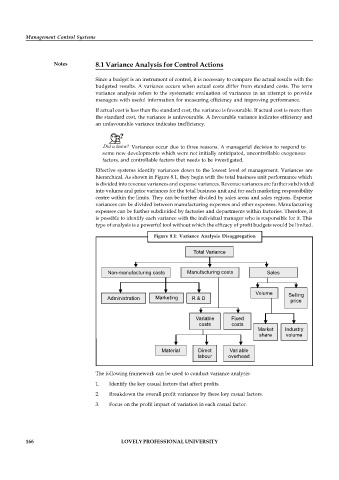
Effective systems identify variances down to the lowest level of management. Variances are
hierarchical. As shown in Figure 8.1, they begin with the total business unit performance which
is divided into revenue variances and expense variances. Revenue variances are further subdivided
into volume and price variances for the total business unit and for each marketing responsibility
centre within the limits. They can be further divided by sales areas and sales regions. Expense
variances can be divided between manufacturing expenses and other expenses. Manufacturing
expenses can be further subdivided by factories and departments within factories. Therefore, it
is possible to identify each variance with the individual manager who is responsible for it. This
type of analysis is a powerful tool without which the efficacy of profit budgets would be limited.
Figure 8.1: Variance Analysis Disaggregation
Total Variance
Non-manufacturing costs Manufacturing costs Sales
Volume Selling
Administration Marketing R & D
price
Variable Fixed
costs costs
Market Industry
share volume
Material Direct Variable
labour overhead
The following framework can be used to conduct variance analysis:
1. Identify the key casual factors that affect profits.
2. Breakdown the overall profit variances by these key casual factors.
3. Focus on the profit impact of variation in each casual factor.
166 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY