Page 80 - DMGT514_MANAGEMENT_CONTROL_SYSTEMS
P. 80
Unit 4: Responsibility Centers
4.8.3 Evaluation of EVA Notes
Advantages of EVA
1. EVA combines profit centre and investment centre concepts. With EVA, management
establishes a target profit or target rate of return for the business segment. Any income in
excess of the target level is the residual income/EVA. To illustrate, the target rate of return
for DD Ltd. is 20 % on total net assets. Total net assets are ` 800,000 and actual net income
` 200,000 so the target net income is 800,000 0.20 = ` 160,000. The EVA for the company is
actual net income minus target net income = ` 200,000 – ` 160,000 = ` 40,000.
2. In case of EVA, different interest rates may be used for different types of assets e.g. low
rates can be used for inventories while a higher rate can be used for investments in fixed
assets. Furthermore, different rates may be used for different fixed assets to take into
account different degrees of risk.
3. With EVA, all business units have the same profit objective for comparable investments.
The ROI approach, on the other hand, provides different incentives for investments across
business units.
4. The EVA in contrast to ROI, has a stronger positive correlation with changes in company's
market share. Shareholders are important stakeholders in a company's market value.
Shareholders are important stakeholders in a company.
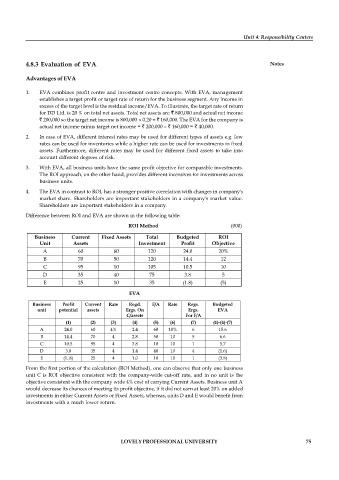
Difference between ROI and EVA are shown in the following table:
ROI Method (000)
Business Current Fixed Assets Total Budgeted ROI
Unit Assets Investment Profit Objective
A 60 60 120 24.0 20%
B 70 50 120 14.4 12
C 95 10 105 10.5 10
D 35 40 75 3.8 5
E 25 10 35 (1.8) (5)
EVA
Business Profit Current Rate Regd. F/A Rate Regs. Budgeted
unit potential assets Ergs. On Ergs. EVA
C/assets For F/A
(1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) (1)-(4)-(7)
A 24.0 60 4% 2.4 60 10% 6 15.6
B 14.4 70 4 2.8 50 10 5 6.6
C 10.5 95 4 3.8 10 10 1 5.7
D 3.8 35 4 1.4 40 10 4 (1.6)
E (1..8) 25 4 1.0 10 10 1 (3.8)
From the first portion of the calculation (ROI Method), one can observe that only one business
unit C is ROI objective consistent with the company-wide cut-off rate, and in no unit is the
objective consistent with the company wide 4% cost of carrying Current Assets. Business unit A
would decrease its chances of meeting its profit objective, if it did not earn at least 20% on added
investments in either Current Assets or Fixed Assets, whereas, units D and E would benefit from
investments with a much lower return.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 75