Page 93 - DMGT518_TRAINING_AND_DEVELOPMENT_SYSTEM
P. 93
Training and Development System
Notes 6.2.3 Human Learning and Memory
Modern work on human learning and memory focuses on the cognitive processes people
use in storing and retrieving information.
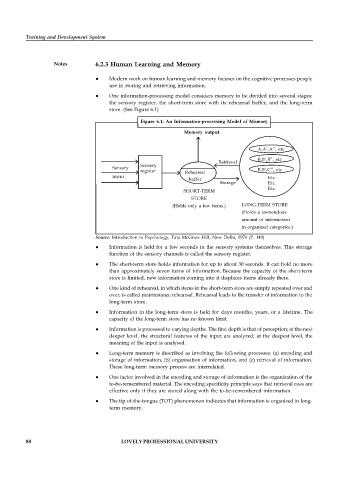
One information-processing model considers memory to be divided into several stages:
the sensory register, the short-term store with its rehearsal buffer, and the long-term
store. (See Figure 6.1)
Figure 6.1: An Information-processing Model of Memory
Memory output
A,A’,A”, etc
B,B’,B”, etc
Retrieval
Sensory
Sensory
register Rehearsal B,B’,C”, etc
input Etc.
buffer
Storage Etc.
Etc.
SHORT-TERM
STORE
(Holds only a few items.) LONG-TERM STORE
(Holds a tremendous
amount of information
in organized categories.)
Source: Introduction to Psychology, Tata McGraw Hill, New Delhi, 1979 (P. 149)
Information is held for a few seconds in the sensory systems themselves. This storage
function of the sensory channels is called the sensory register.
The short-term store holds information for up to about 30 seconds. It can hold no more
than approximately seven items of information. Because the capacity of the short-term
store is limited, new information coming into it displaces items already there.
One kind of rehearsal, in which items in the short-term store are simply repeated over and
over, is called maintenance rehearsal. Rehearsal leads to the transfer of information to the
long-term store.
Information in the long-term store is held for days months, years, or a lifetime. The
capacity of the long-term store has no known limit.
Information is processed to varying depths. The first depth is that of perception; at the next
deeper level, the structural features of the input are analyzed; at the deepest level, the
meaning of the input is analysed.
Long-term memory is described as involving the following processes: (a) encoding and
storage of information, (b) organisation of information, and (c) retrieval of information.
These long-term memory process are interrelated.
One factor involved in the encoding and storage of information is the organisation of the
to-be-remembered material. The encoding specificity principle says that retrieval cues are
effective only if they are stored along with the to-be-remembered information.
The tip-of-the-tongue (TOT) phenomenon indicates that information is organised in long-
term memory.
88 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY