Page 94 - DMGT518_TRAINING_AND_DEVELOPMENT_SYSTEM
P. 94
Unit 6: Learning Theories
Retrieval from long-term memory, is a two-stage process. In the first stage, a “reminder” Notes
triggers the generation of the search through the categories of long-term memory; the
second stage is the recognition of the searched-for item of information when it is contacted.
Forgetting from long-term memory is the apparent loss of information that has already
been stored. Inadequate encoding, poor organisation, and difficulties with retrieval lead
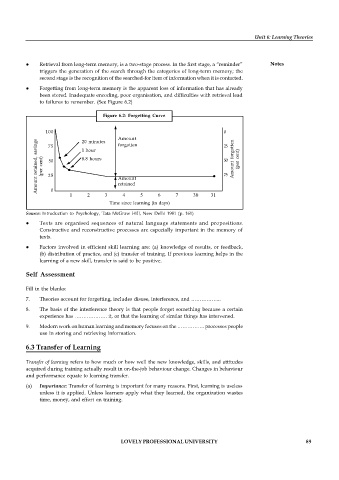
to failures to remember. (See Figure 6.2)
Figure 6.2: Forgetting Curve
100 0
Amount 25
Amount retained, savings (per cent) 50 8.8 hours Amount 50 Amount forgotten (per cent)
20 minutes
forgotten
75
1 hour
75
25
0
4
1 2 3 retained 5 6 7 30 31
Time since learning (in days)
Source: Introduction to Psychology, Tata McGraw Hill, New Delhi 1981 (p. 161)
Texts are organised sequences of natural language statements and propositions.
Constructive and reconstructive processes are especially important in the memory of
texts.
Factors involved in efficient skill learning are: (a) knowledge of results, or feedback,
(b) distribution of practice, and (c) transfer of training. If previous learning helps in the
learning of a new skill, transfer is said to be positive.
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
7. Theories account for forgetting, includes disuse, interference, and ……………...
8. The basis of the interference theory is that people forget something because a certain
experience has ………………. it, or that the learning of similar things has intervened.
9. Modern work on human learning and memory focuses on the ……………. processes people
use in storing and retrieving information.
6.3 Transfer of Learning
Transfer of learning refers to how much or how well the new knowledge, skills, and attitudes
acquired during training actually result in on-the-job behaviour change. Changes in behaviour
and performance equate to learning transfer.
(a) Importance: Transfer of learning is important for many reasons. First, learning is useless
unless it is applied. Unless learners apply what they learned, the organization wastes
time, money, and effort on training.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 89