Page 97 - DMGT518_TRAINING_AND_DEVELOPMENT_SYSTEM
P. 97
Training and Development System
Notes
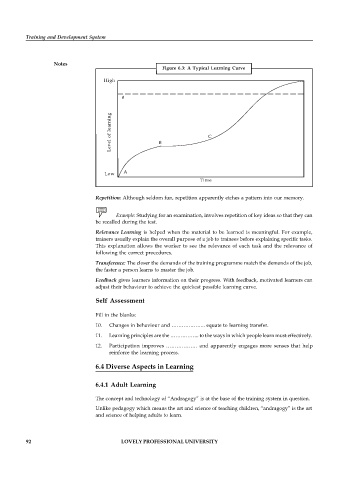
Figure 6.3: A Typical Learning Curve
High
0
Level of learning B C
Low A
Time
Repetition: Although seldom fun, repetition apparently etches a pattern into our memory.
Example: Studying for an examination, involves repetition of key ideas so that they can
be recalled during the test.
Relevance Learning is helped when the material to be learned is meaningful. For example,
trainers usually explain the overall purpose of a job to trainees before explaining specific tasks.
This explanation allows the worker to see the relevance of each task and the relevance of
following the correct procedures.
Transference: The closer the demands of the training programme match the demands of the job,
the faster a person learns to master the job.
Feedback gives learners information on their progress. With feedback, motivated learners can
adjust their behaviour to achieve the quickest possible learning curve.
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
10. Changes in behaviour and ……………….. equate to learning transfer.
11. Learning principles are the …………….. to the ways in which people learn must effectively.
12. Participation improves ……………… and apparently engages more senses that help
reinforce the learning process.
6.4 Diverse Aspects in Learning
6.4.1 Adult Learning
The concept and technology of “Andragogy” is at the base of the training system in question.
Unlike pedagogy which means the art and science of teaching children, “andragogy” is the art
and science of helping adults to learn.
92 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY