Page 128 - DMGT524_TOTAL_QUALITY_MANAGEMENT
P. 128
Unit 9: Benchmarking
Organizations need to improve continuously in various areas to keep them in a competitive Notes
position. They can learn from various sources for their continuous improvement. Learning can
be from both internal and external sources. Many firms choose to compare their performance
against that of another firm in order to learn how they are performing in the market place. This
can help them measure not only in understanding their current performance, but also help them
in best practices in other organizations from which they can learn and improve. Thus
benchmarking best industry practices is one of the popular quality management methodology
used by organizations all over the world. Xerox was the first organization which initiated
benchmarking concept and it went on win Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award. Xerox
basically studied best practices of its competitors to learn and improve its own performance.
Since then many other organizations have used benchmarking as tool for quality and productivity
improvement.
9.1 Definition of Benchmarking
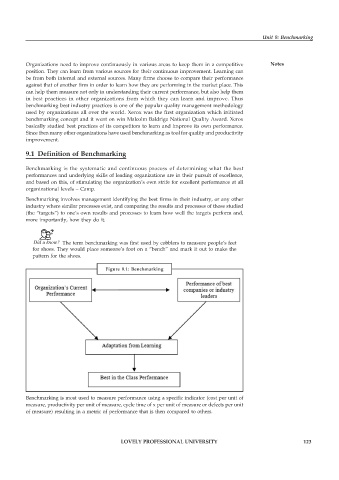
Benchmarking is the systematic and continuous process of determining what the best
performances and underlying skills of leading organizations are in their pursuit of excellence,
and based on this, of stimulating the organization’s own strife for excellent performance at all
organizational levels – Camp.
Benchmarking involves management identifying the best firms in their industry, or any other
industry where similar processes exist, and comparing the results and processes of those studied
(the “targets”) to one’s own results and processes to learn how well the targets perform and,
more importantly, how they do it.
Did u know? The term benchmarking was first used by cobblers to measure people’s feet
for shoes. They would place someone’s foot on a “bench” and mark it out to make the
pattern for the shoes.
Figure 9.1: Benchmarking
Benchmarking is most used to measure performance using a specific indicator (cost per unit of
measure, productivity per unit of measure, cycle time of x per unit of measure or defects per unit
of measure) resulting in a metric of performance that is then compared to others.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 123