Page 210 - DMGT524_TOTAL_QUALITY_MANAGEMENT
P. 210
Unit 14: Statistical Process Control
four possible outcomes that can arise when natural process variability is compared with product Notes
specs. In Figure 14.4 the specifications are wider than the natural variation; one would therefore
expect that this process will always produce conforming products as long as it remains in
control. It may even be possible to reduce costs by investing in a cheaper technology that
permits a larger variation in the process output. In Figure 14.5, the natural variation and
specifications are the same. A small percentage of nonconforming products might be produced;
thus, the process should be closely monitored.
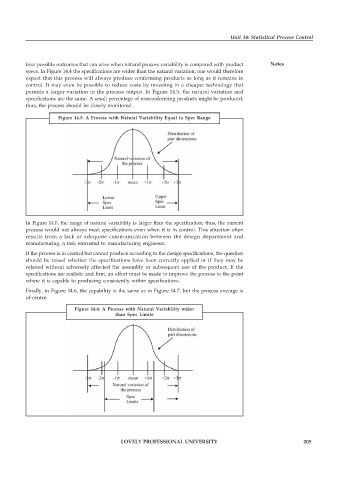
Figure 14.5: A Process with Natural Variability Equal to Spec Range
In Figure 14.6, the range of natural variability is larger than the specification; thus, the current
process would not always meet specifications even when it is in control. This situation often
results from a lack of adequate communication between the design department and
manufacturing, a task entrusted to manufacturing engineers.
If the process is in control but cannot produce according to the design specifications, the question
should be raised whether the specifications have been correctly applied or if they may be
relaxed without adversely affected the assembly or subsequent use of the product. If the
specifications are realistic and firm, an effort must be made to improve the process to the point
where it is capable to producing consistently within specifications.
Finally, in Figure 14.6, the capability is the same as in Figure 14.7, but the process average is
of-centre.
Figure 14.6: A Process with Natural Variability wider
than Spec Limits
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 205