Page 147 - DMGT525_MATERIALS_MANAGEMENT
P. 147
Materials Management
Notes All functions to the right of the basic function portray the conceptual approach selected to satisfy
the basic function. The concept describes the method being considered, or elected, to achieve the
basic function. The concept can represent either the current conditions (as is) or proposed approach
(to be). As a general rule, it is best to create a “to be” rather than an “as is” FAST Model, even if
the assignment is to improve an existing product. This approach will give the product
development team members an opportunity to compare the “ideal” to the “current” and help
resolve how to implement the differences. Working from an “as is” model will restrict the
team’s attention to incremental improvement opportunities. An “as is” model is useful for
tracing the symptoms of a problem to its root cause, and exploring ways to resolve the problem,
because of the dependent relationship of functions that form the FAST model.
Any function on the HOW-WHY logic path is a logic path function. If the functions along the
WHY direction lead into the basic function, than they are located on the major logic path. If the
WHY path does not lead directly to the basic function, it is a minor logic path. Changing a
function on the major logic path will alter or destroy the way the basic function is performed.
Changing a function on a minor logic path will disturb an independent (supporting) function
that enhances the basic function. Supporting functions are usually secondary and exist to achieve
the performance levels specified in the objectives or specifications of the basic functions or
because a particular approach was chosen to implement the basic function.
Independent functions describe an enhancement or control of a function located on the logic
path. They do not depend on another function or method selected to perform that function.
Independent functions are located above the logic path function, and are considered secondary,
with respect to the scope, nature, level of the problem, and its logic path.
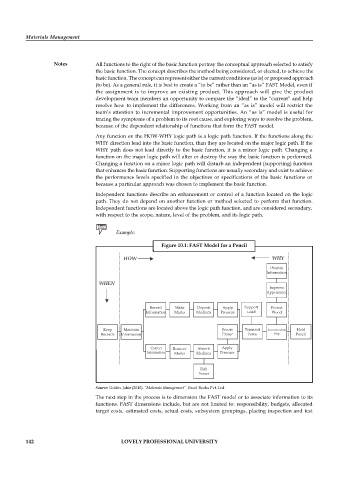
Example:
Figure 10.1: FAST Model for a Pencil
HOW WHY
Display
Information
WHEN
Improve
Appearance
Record Make Deposit Apply Support Protect
Information Marks Medium Pressure Lead Wood
Keep Maintain Secure Transmit Accommodate Hold
Records Information Eraser Force Grip Pencil
Correct Remove Absorb Apply
Information Marks Medium Pressure
Rub
Eraser
Source: Uddin. Jahir (2010). “Materials Management”. Excel Books Pvt. Ltd.
The next step in the process is to dimension the FAST model or to associate information to its
functions. FAST dimensions include, but are not limited to: responsibility, budgets, allocated
target costs, estimated costs, actual costs, subsystem groupings, placing inspection and test
142 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY