Page 22 - DMGT525_MATERIALS_MANAGEMENT
P. 22
Unit 2: ABC Analysis
To help someone change their behaviour, it is a simple matter to develop consequences Notes
that are encouraging, immediate, highly important and consistently applied. CLG teaches
the E-TIP Analysis to clients to help them determine which encouragers or discouragers
are going to have the most effect.
Source: http://www.clg.com/Science-Of-Success/CLG-Methodology/Behavior-Change-Tools/ABC-
ETIP.aspx
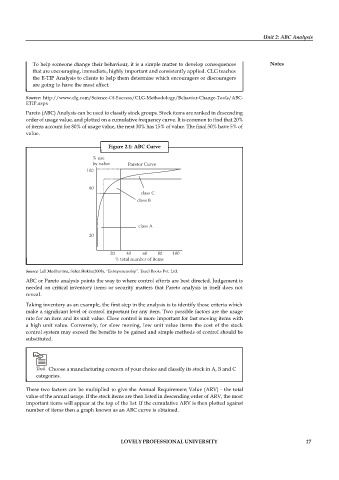
Pareto (ABC) Analysis can be used to classify stock groups. Stock items are ranked in descending
order of usage value, and plotted on a cumulative frequency curve. It is common to find that 20%
of items account for 80% of usage value, the next 30% has 15% of value. The final 50% have 5% of
value.
Figure 2.1: ABC Curve
% use
by value Paretor Curve
100
80
class C
class B
class A
20
20 40 60 80 100
% total number of items
Source: Lall.Madhurima, Sahai.Shikha(2008), “Entrepreneurship”. Excel Books Pvt. Ltd.
ABC or Pareto analysis points the way to where control efforts are best directed. Judgement is
needed on critical inventory items or security matters that Pareto analysis in itself does not
reveal.
Taking inventory as an example, the first step in the analysis is to identify those criteria which
make a significant level of control important for any item. Two possible factors are the usage
rate for an item and its unit value. Close control is more important for fast moving items with
a high unit value. Conversely, for slow moving, low unit value items the cost of the stock
control system may exceed the benefits to be gained and simple methods of control should be
substituted.
Task Choose a manufacturing concern of your choice and classify its stock in A, B and C
categories.
These two factors can be multiplied to give the Annual Requirement Value (ARV) - the total
value of the annual usage. If the stock items are then listed in descending order of ARV, the most
important items will appear at the top of the list. If the cumulative ARV is then plotted against
number of items then a graph known as an ABC curve is obtained.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 17