Page 212 - DMGT549_INTERNATIONAL_FINANCIAL_MANAGEMENT
P. 212
Unit 12: Foreign Market Entry and Country Risk Management
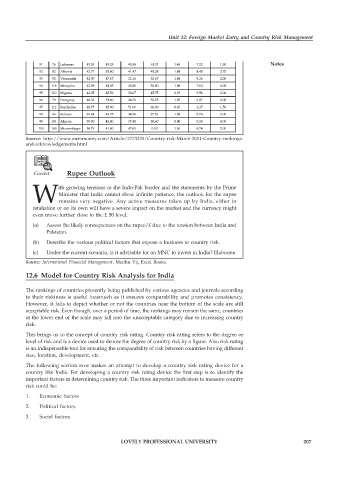
91 76 Lebanon 43.53 45.25 45.58 61.31 1.46 7.22 1.50 Notes
92 82 Albania 42.77 38.00 41.47 48.38 1.88 8.48 3.75
93 92 Venezuela 42.47 47.67 32.16 53.67 1.88 9.30 2.00
94 118 Mongolia 42.09 44.33 40.85 30.00 1.88 7.63 4.00
95 110 Nigeria 42.05 45.56 33.67 45.75 2.19 9.54 2.00
96 79 Paraguay 40.33 51.00 24.70 53.25 1.25 9.07 2.00
97 112 Seychelles 40.27 45.00 51.00 60.00 0.63 3.37 1.50
98 96 Belarus 39.84 43.75 34.38 27.81 1.88 8.73 3.00
99 101 Algeria 39.50 45.80 37.40 50.60 0.00 5.50 4.00
100 100 Mozambique 38.79 41.00 47.00 0.00 1.56 8.74 2.00
Source: http://www.euromoney.com/Article/2773235/Country-risk-March-2011-Country-rankings-
and-acknowledgements.html
Caselet Rupee Outlook
ith growing tensions at the Indo-Pak border and the statements by the Prime
Minister that India cannot show infinite patience, the outlook for the rupee
Wremains very negative. Any active measures taken up by India, either in
retaliation or on its own will have a severe impact on the market and the currency might
even move further close to the £ 50 level.
(a) Assess the likely consequences on the rupee/£ due to the tension between India and
Pakistan.
(b) Describe the various political factors that expose a business to country risk.
(c) Under the current scenario, is it advisable for an MNC to invest in India? Elaborate.
Source: International Financial Management, Madhu Vij, Excel Books.
12.6 Model for Country Risk Analysis for India
The rankings of countries presently being published by various agencies and journals according
to their riskiness is useful inasmuch as it ensures comparability and promotes consistency.
However, it fails to depict whether or not the countries near the bottom of the scale are still
acceptable risk. Even though, over a period of time, the rankings may remain the same, countries
at the lower end of the scale may fall into the unacceptable category due to increasing country
risk.
This brings us to the concept of country risk rating. Country risk rating refers to the degree or
level of risk and is a device used to denote the degree of country risk by a figure. Also risk rating
is an indispensable tool for ensuring the comparability of risk between countries having different
size, location, development, etc.
The following section now makes an attempt to develop a country risk rating device for a
country like India. For developing a country risk rating device the first step is to identify the
important factors in determining country risk. The three important indicators to measure country
risk could be:
1. Economic factors
2. Political factors
3. Social factors
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 207