Page 256 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 256
Unit-13: Theory of Monopoly Firm
13.4 Total Revenue and Total Cost Curve Approach Notes
Monopolist can achieve maximum profit by selling that particular quantity of goods at which the
difference between total revenue and total cost would be maximum. A monopolist by projecting
different prices of any goods or by altering the supply of goods, tries to understand that at which
level of output the difference between total revenue (TR) and total cost (TC) would be maximum, or
total profit would be maximum. At that quantity of output producing which monopolist will get the
maximum profit, monopolist will be at equilibrium. It can be explained with the help of Fig. 13.1.
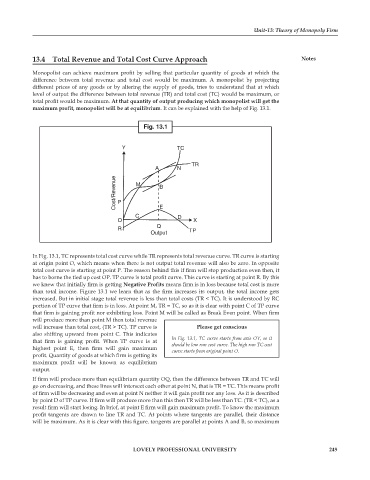
Fig. 13.1
Y TC
TR
A N
Cost/Revenue P M B
C E D
O X
Q
R TP
Output
In Fig. 13.1, TC represents total cost curve while TR represents total revenue curve. TR curve is starting
at origin point O, which means when there is not output total revenue will also be zero. In opposite
total cost curve is starting at point P. The reason behind this if firm will stop production even then, it
has to borne the tied up cost OP. TP curve is total profit curve. This curve is starting at point R. By this
we knew that initially firm is getting Negative Profits means firm is in loss because total cost is more
than total income. Figure 13.1 we learn that as the firm increases its output, the total income gets
increased. But in initial stage total revenue is less than total costs (TR < TC). It is understood by RC
portion of TP curve that firm is in loss. At point M, TR = TC, so as it is clear with point C of TP curve
that firm is gaining profit nor exhibiting loss. Point M will be called as Break Even point. When firm
will produce more than point M then total revenue
will increase than total cost, (TR > TC). TP curve is Please get conscious
also shifting upward from point C. This indicates
that firm is gaining profit. When TP curve is at In Fig. 13.1, TC curve starts from axis OY, so it
highest point E, then firm will gain maximum should be low run cost curve. The high run TC cost
curve starts from original point O.
profit. Quantity of goods at which firm is getting its
maximum profit will be known as equilibrium
output.
If firm will produce more than equilibrium quantity OQ, then the difference between TR and TC will
go on decreasing, and these lines will intersect each other at point N, that is TR = TC. This means profit
of firm will be decreasing and even at point N neither it will gain profit nor any loss. As it is described
by point D of TP curve. If firm will produce more than this then TR will be less than TC. (TR < TC), as a
result firm will start losing. In brief, at point E firm will gain maximum profit. To know the maximum
profit tangents are drawn to line TR and TC. At points where tangents are parallel, their distance
will be maximum. As it is clear with this figure. tangents are parallel at points A and B, so maximum
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 249