Page 259 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 259
Microeconomic Theory
Notes production of the monopolist is OM units. Average Cost Curve (AC) touches Average Revenue Curve
(AR) at point A at this level production is at point A, Price OP (AR) of the product is equal to average
cost AM (AC) so the monopolist will earn only Normal Profits at equilibrium production because at
equilibrium quantity and average cost are equal to price (Average Income) (AC = AR).
(3) Minimum Loss: In short run, demand of the goods decreases due to depression and as a result prices
fall the monopolist will continue to produce at this reduced price if he is getting Average variable cost
(AVC) at this price. If the monopolist will have to determine the prices less than the average variable cost
then he will stop the production. Therefore, the monopolist in the short run may have to bear minimum
loss means can bear loss of average fixed cost. In equilibrium situation prices (AR) of the product is
equal to Average variable cost (AVC) so the monopolist may have to bear average fixed cost loss. This
loss has to bear by monopolist even at the time when he stops work during short run. Therefore.,
Minimum Loss = AC – AVC = AFC
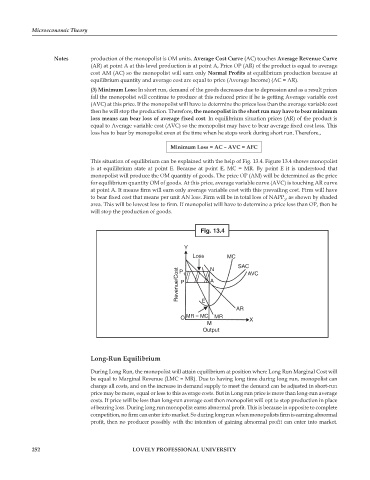
This situation of equilibrium can be explained with the help of Fig. 13.4. Figure 13.4 shows monopolist
is at equilibrium state at point E. Because at point E, MC = MR. By point E it is understood that
monopolist will produce the OM quantity of goods. The price OP (AM) will be determined as the price
for equilibrium quantity OM of goods. At this price, average variable curve (AVC) is touching AR curve
at point A. It means firm will earn only average variable cost with this prevailing cost. Firm will have
to bear fixed cost that means per unit AN loss. Firm will be in total loss of NAPP , as shown by shaded
1
area. This will be lowest loss to firm. If monopolist will have to determine a price less than OP, then he
will stop the production of goods.
Fig. 13.4
Y
Loss MC
SAC AVC
Revenue/Cost P A
N
P
1
E
AR
O MR = MC MR X
M
Output
Long-Run Equilibrium
During Long Run, the monopolist will attain equilibrium at position where Long Run Marginal Cost will
be equal to Marginal Revenue (LMC = MR). Due to having long time during long run, monopolist can
change all costs, and on the increase in demand supply to meet the demand can be adjusted in short-run
price may be more, equal or less to this average costs. But in Long run price is more than long-run average
costs. If price will be less than long-run average cost then monopolist will opt to stop production in place
of bearing loss. During long run monopolist earns abnormal profit. This is because in opposite to complete
competition, no firm can enter into market. So during long run when monopolists firm is earning abnormal
profit, then no producer possibly with the intention of gaining abnormal profit can enter into market.
252 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY