Page 260 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 260
Unit-13: Theory of Monopoly Firm
As a result, monopolist firm earns abnormal profit Notes
even at the time of long run. In opposite to complete Unlike to full competitive firm a monopolist can
competent firm, monopolist can earn abnormal profit earn abnormal profit in the long term because there
during long run, because the entrance of new firm is a ban on the entry to new firm into the market.
in market is restricted. Thus the monopoly firm gets
abnormal profits in long run.
In market monopolist, neither due to the entrance of any firm nor due to availability of any substitute
is required to set up an optimum sized plant or to utilize optimum production capacity during long
run. Size of plant or the utilization upto which extent of any particular size plant, is always dependent
on the demand in market. Under same market situation optimum capacity will be achieved but under
some other situations monopolist will produce sub optimally. Under some different situations capacity
more than optimum capacity can be utilized. It all depends on the demand in market. In Fig. 13.5,
the maximum long run equilibrium has been explained, when size of market restricts monopolist to
produce at minimum long-run average cost.
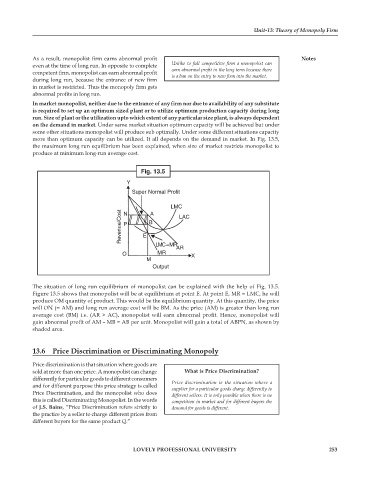
Fig. 13.5
Y
Super Normal Profit
LMC
Revenue/Cost P E B LAC
N
A
LMC = MR
AR
O MR X
M
Output
The situation of long run equilibrium of monopolist can be explained with the help of Fig. 13.5.
Figure 13.5 shows that monopolist will be at equilibrium at point E. At point E, MR = LMC, he will
produce OM quantity of product. This would be the equilibrium quantity. At this quantity, the price
will ON (= AM) and long run average cost will be BM. As the price (AM) is greater than long run
average cost (BM) i.e. (AR > AC), monopolist will earn abnormal profit. Hence, monopolist will
gain abnormal profit of AM – MB = AB per unit. Monopolist will gain a total of ABPN, as shown by
shaded area.
13.6 Price Discrimination or Discriminating Monopoly
Price discrimination is that situation where goods are
sold at more than one price. A monopolist can change What is Price Discrimination?
differently for particular goods to different consumers
and for different purpose this price strategy is called Price discrimination is the situation where a
Price Discrimination, and the monopolist who does supplier for a particular goods charge differently to
different sellers. It is only possible when there is no
this is called Discriminating Monopolist. In the words competition in market and for different buyers the
of J.S. Bains, “Price Discrimination refers strictly to demand for goods is different.
the practice by a seller to charge different prices from
different buyers for the same product Q.”
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 253