Page 258 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 258
Unit-13: Theory of Monopoly Firm
Notes
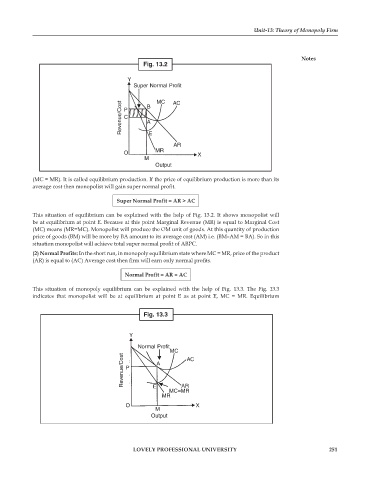
Fig. 13.2
Y
Super Normal Profit
Revenue/Cost P B MC AC
C
A
E
AR
MR
O X
M
Output
(MC = MR). It is called equilibrium production. If the price of equilibrium production is more than its
average cost then monopolist will gain super normal profit.
Super Normal Profit = AR > AC
This situation of equilibrium can be explained with the help of Fig. 13.2. It shows monopolist will
be at equilibrium at point E. Because at this point Marginal Revenue (MR) is equal to Marginal Cost
(MC) means (MR=MC). Monopolist will produce the OM unit of goods. At this quantity of production
price of goods (BM) will be more by BA amount to its average cost (AM) i.e. (BM–AM = BA). So in this
situation monopolist will achieve total super normal profit of ABPC.
(2) Normal Profits: In the short run, in monopoly equilibrium state where MC = MR, price of the product
(AR) is equal to (AC) Average cost then firm will earn only normal profits.
Normal Profit = AR = AC
This situation of monopoly equilibrium can be explained with the help of Fig. 13.3. The Fig. 13.3
indicates that monopolist will be at equilibrium at point E as at point E, MC = MR. Equilibrium
Fig. 13.3
Y
Normal Profit
MC AC
Revenue/Cost P A
AR
E
MC=MR
MR
O X
M
Output
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 251