Page 408 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 408
Unit-29: Insurance Choice and Risk
Just think about a person who has a bike of ` 50,000. He buys a policy of ` 5,000 for protecting his bike Notes
from theft, accident etc. He assumes that the probability of theft is 0.1 and expected loss is ` 5,000 (= 0.10
× ` 50,000). Since the cost of policy ` 5,000 is equal to expected loss ` 5,000, so he will buy policy to get
rid from risk that if the bike has stolen he can get the full amount of bike.
The risk averse people has two options—(1) if he does not take policy then the probability of fault is 0.1
means ` 5,000 (2) If he takes policy then there is no scope of loss of ` 50,000. He pays ` 5,000 as policy
premium and gets profit of ` 45,000 as 0.9 probability. A risk averse by doing this kind of action, got ends
the risk. But an insurance company wants to get profit. So it does not imply the fair laws as stated above. It
takes more premiums, let’s assume ` 5,500. ` 500 is its cost and it is actually its profit or income.
Like all persons, a risk averse person has also marginal utility of capital. When he buys a insurance
policy after the probability of 0.1, he thinks the risk low amount as decrease of his wealth.
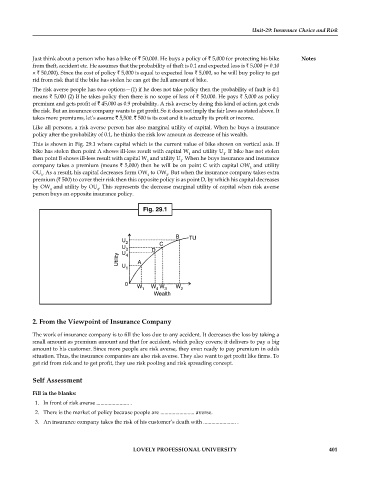
This is shown in Fig. 29.1 where capital which is the current value of bike shown on vertical axis. If
bike has stolen then point A shows ill-less result with capital W and utility U . If bike has not stolen
1
1
then point B shows ill-less result with capital W and utility U . When he buys insurance and insurance
2
2
company takes a premium (means ` 5,000) then he will be on point C with capital OW and utility
3
OU . As a result, his capital decreases form OW to OW . But when the insurance company takes extra
3
3
2
premium (` 500) to cover their risk then this opposite policy is as point D, by which his capital decreases
by OW and utility by OU . This represents the decrease marginal utility of capital when risk averse
4
4
person buys an opposite insurance policy.
Fig. 29.1
B TU
U
2 C
U 3 D
Utility U 4 A
U
1
0
W W W W
1 4 3 2
Wealth
2. From the Viewpoint of Insurance Company
The work of insurance company is to fill the loss due to any accident. It decreases the loss by taking a
small amount as premium amount and that for accident, which policy covers; it delivers to pay a big
amount to his customer. Since more people are risk averse, they even ready to pay premium in odds
situation. Thus, the insurance companies are also risk averse. They also want to get profit like firms. To
get rid from risk and to get profit, they use risk pooling and risk spreading concept.
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
1. In front of risk averse ........................ .
2. There is the market of policy because people are ......................... averse.
3. An insurance company takes the risk of his customer’s death with ........................ .
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 401