Page 411 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 411
Microeconomic Theory
Notes 2. Adverse Selection
When insurance company knows less for the future incidents from the customer, then it creates adverse
selection like personal illness insurance market. In this, the person knows more from the insurance
policy, which however check his health while insured him. So the insurance company takes premium
on the basis of national average. He will motivate more ill people to get insured than less fit people.
On the other hand, fit people thinks that he is about to pay more against his low individual risk.
Other hand, the ill people think that he is paying fewer premiums against his high risk. As a result,
the higher risk people buy more insurance while lower risk people do not buy insurance. This is the
problem of adverse selection which will bankrupt the insurance companies. This condition makes the
high premium in insurance and thus the ill people stop getting insurance because they think that the
individual payment is lower than policy premium.
To getting rid from this adverse selection problem, the insurance company gets various premiums on
the basis of various age limits and the nature of risk for industries. Thus the premium amount is more
for high risk people than the low risk people. To solve the adverse selection, the insurance company
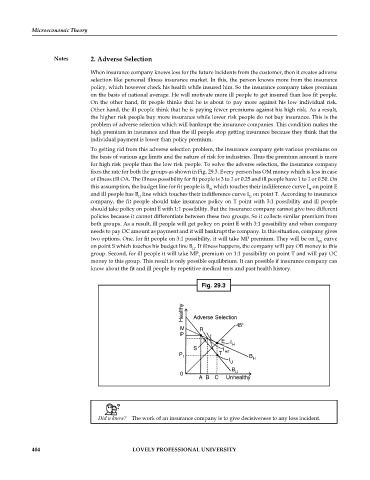
fixes the rate for both the groups as shown in Fig. 29.3. Every person has OM money which is less in case
of illness till OA. The illness possibility for fit people is 3 to 1 or 0.25 and ill people have 1 to 1 or 0.50. On
this assumption, the budget line for fit people is B which touches their indifference curve I on point E
H
H
and ill people has B line which touches their indifference curve I on point T. According to insurance
U
U
company, the fit people should take insurance policy on T point with 3:1 possibility and ill people
should take policy on point E with 1:1 possibility. But the insurance company cannot give two different
policies because it cannot differentiate between these two groups. So it collects similar premium from
both groups. As a result, ill people will get policy on point E with 3:1 possibility and when company
needs to pay OC amount as payment and it will bankrupt the company. In this situation, company gives
two options. One, for fit people on 3:1 possibility, it will take MP premium. They will be on I curve
H1
on point S which touches his budget line B . If illness happens, the company will pay OB money to this
H
group. Second, for ill people it will take MP premium on 1:1 possibility on point T and will pay OC
1
money to this group. This result is only possible equilibrium. It can possible if insurance company can
know about the fit and ill people by repetitive medical tests and past health history.
Fig. 29.3
Healthy Adverse Selection
45°
M R
P
E I H
S I
P T H1
1 B H
I
U
B U
0
AB C Unhealthy
The work of an insurance company is to give decisiveness to any loss incident.
404 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY