Page 6 - DECO402_MACROECONOMIC_THEORY_PUNJABI
P. 6
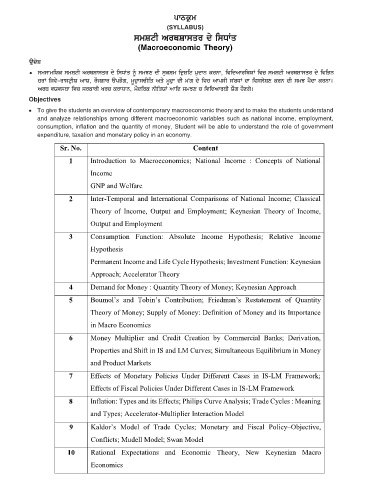
Í≈·¥Ó
(SYLLABUS)
smStI ArQSwsqr dy isDWq
(Macroeconomic Theory)
¿πÁ∂Ù
J smswmiXk smStI ArQSwsqr dy isDWq ƒ smJx dI sukSm id®Sit p®dwn krnw, ividAwriQXW ivc smStI ArQSwsqr dy iviBn
crW ijvy–rwst®IX AwX, rOjgwr apBOg, mUd®wsFIiq Aqy mUd®w dI mNg dy ivc AwpsI sNbDW dw ivslySx krn dI smJ pYdw krnw[
ArQ vXvsQw ivc srkwrI Krc krwDwn, mOdirk nIiqXW Awid smJx c ividAwrQI XOg hOxgy[
Objectives
J To give the students an overview of contemporary macroeconomic theory and to make the students understand
and analyze relationships among different macroeconomic variables such as national income, employment,
consumption, inflation and the quantity of money, Student will be able to understand the role of government
expenditure, taxation and monetary policy in an economy.
Sr. No. Content
1 Introduction to Macroeconomics; National Income : Concepts of National
Income
GNP and Welfare
2 Inter-Temporal and International Comparisons of National Income; Classical
Theory of Income, Output and Employment; Keynesian Theory of Income,
Output and Employment
3 Consumption Function: Absolute Income Hypothesis; Relative Income
Hypothesis
Permanent Income and Life Cycle Hypothesis; Investment Function: Keynesian
Approach; Accelerator Theory
4 Demand for Money : Quantity Theory of Money; Keynesian Approach
5 Boumol’s and Tobin’s Contribution; Friedman’s Restatement of Quantity
Theory of Money; Supply of Money: Definition of Money and its Importance
in Macro Economics
6 Money Multiplier and Credit Creation by Commercial Banks; Derivation,
Properties and Shift in IS and LM Curves; Simultaneous Equilibrium in Money
and Product Markets
7 Effects of Monetary Policies Under Different Cases in IS-LM Framework;
Effects of Fiscal Policies Under Different Cases in IS-LM Framework
8 Inflation: Types and its Effects; Philips Curve Analysis; Trade Cycles : Meaning
and Types; Accelerator-Multiplier Interaction Model
9 Kaldor’s Model of Trade Cycles; Monetary and Fiscal Policy–Objective,
Conflicts; Mudell Model; Swan Model
10 Rational Expectations and Economic Theory, New Keynesian Macro
Economics