Page 186 - DECO504_STATISTICAL_METHODS_IN_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 186
Statistical Methods in Economics
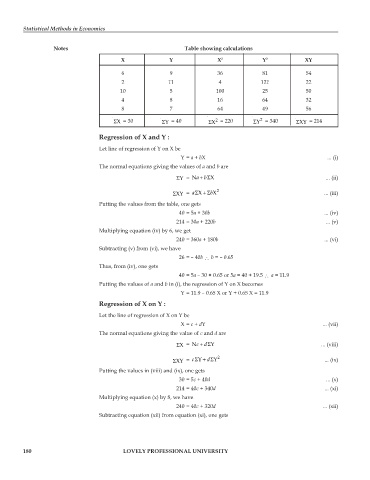
Notes Table showing calculations
X Y X 2 Y 2 XY
6 9 36 81 54
2 11 4 121 22
10 5 100 25 50
4 8 16 64 32
8 7 64 49 56
2
ΣX = 30 ΣY = 40 ΣX 2 = 220 ΣY = 340 ΣXY = 214
Regression of X and Y :
Let line of regression of Y on X be
Y= a + bX ... (i)
The normal equations giving the values of a and b are
ΣY = Nab ... (ii)
+ΣX
ΣXY = Σ+ ΣXa b X 2 ... (iii)
Putting the values from the table, one gets
40 = 5a + 30b ... (iv)
214 = 30a + 220b ... (v)
Multiplying equation (iv) by 6, we get
240 = 360a + 180b ... (vi)
Subtracting (v) from (vi), we have
26 = – 40b ∴ b = – 0.65
Thus, from (iv), one gets
40 = 5a – 30 × 0.65 or 5a = 40 + 19.5 ∴ a = 11.9
Putting the values of a and b in (i), the regression of Y on X becomes
Y = 11.9 – 0.65 X or Y + 0.65 X = 11.9
Regression of X on Y :
Let the line of regression of X on Y be
X= c + dY ... (vii)
The normal equations giving the value of c and d are
+ΣY
ΣX = Ncd ... (viii)
ΣXY = Σ+ ΣYc d Y 2 ... (ix)
Putting the values in (viii) and (ix), one gets
30 = 5c + 40d ... (x)
214 = 40c + 340d ... (xi)
Multiplying equation (x) by 8, we have
240 = 40c + 320d ... (xii)
Subtracting equation (xii) from equation (xi), one gets
180 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY