Page 248 - DECO504_STATISTICAL_METHODS_IN_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 248
Statistical Methods in Economics
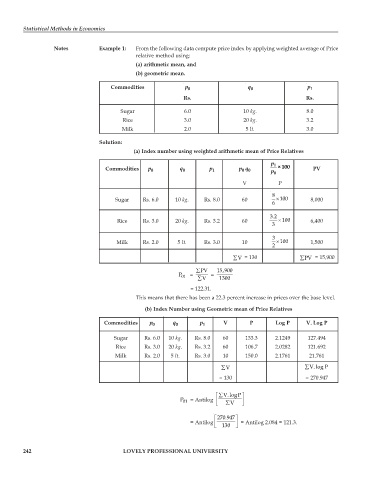
Notes Example 1: From the following data compute price index by applying weighted average of Price
relative method using:
(a) arithmetic mean, and
(b) geometric mean.
Commodities p 0 q 0 p 1
Rs. Rs.
Sugar 6.0 10 kg. 8.0
Rice 3.0 20 kg. 3.2
Milk 2.0 5 lt. 3.0
Solution:
(a) Index number using weighted arithmetic mean of Price Relatives
p 1
Commodities p 0 q 0 p 1 pq p 0 ×100 PV
00
V P
8
Sugar Rs. 6.0 10 kg. Rs. 8.0 60 × 100 8,000
6
3.2
Rice Rs. 3.0 20 kg. Rs. 3.2 60 × 100 6,400
3
3
Milk Rs. 2.0 5 lt. Rs. 3.0 10 × 100 1,500
2
∑ V = 130 ∑ PV = 15,900
∑ PV 15,900
P 01 = ∑ V = 1300
= 122.31.
This means that there has been a 22.3 percent increase in prices over the base level.
(b) Index Number using Geometric mean of Price Relatives
Commodities p 0 q 0 p 1 V P Log P V. Log P
Sugar Rs. 6.0 10 kg. Rs. 8.0 60 133.3 2.1249 127.494
Rice Rs. 3.0 20 kg. Rs. 3.2 60 106.7 2.0282 121.692
Milk Rs. 2.0 5 lt. Rs. 3.0 10 150.0 2.1761 21.761
∑ V ∑ V. log P
= 130 = 270.947
⎡ ∑ V. logP ⎤
P 01 = Antilog ⎢ ⎣ ∑ V ⎥ ⎦
⎡ 270.947 ⎤
= Antilog ⎢ ⎥ = Antilog 2.084 = 121.3.
⎣ 130 ⎦
242 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY