Page 249 - DECO504_STATISTICAL_METHODS_IN_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 249
Unit 19: Methods—Weighted Average of Price Relatives
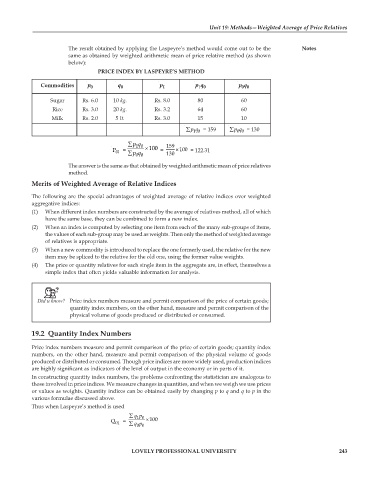
The result obtained by applying the Laspeyre’s method would come out to be the Notes
same as obtained by weighted arithmetic mean of price relative method (as shown
below):
PRICE INDEX BY LASPEYRE’S METHOD
Commodities p 0 q 0 p 1 p q p q
00
1 0
Sugar Rs. 6.0 10 kg. Rs. 8.0 80 60
Rice Rs. 3.0 20 kg. Rs. 3.2 64 60
Milk Rs. 2.0 5 lt. Rs. 3.0 15 10
∑ pq = 159 ∑ pq = 130
10
00
∑ pq 159
10
P 01 = ∑ pq × 100 = 130 × 100 = 122.31
00
The answer is the same as that obtained by weighted arithmetic mean of price relatives
method.
Merits of Weighted Average of Relative Indices
The following are the special advantages of weighted average of relative indices over weighted
aggregative indices:
(1) When different index numbers are constructed by the average of relatives method, all of which
have the same base, they can be combined to form a new index.
(2) When an index is computed by selecting one item from each of the many sub-groups of items,
the values of each sub-group may be used as weights. Then only the method of weighted average
of relatives is appropriate.
(3) When a new commodity is introduced to replace the one formerly used, the relative for the new
item may be spliced to the relative for the old one, using the former value weights.
(4) The price or quantity relatives for each single item in the aggregate are, in effect, themselves a
simple index that often yields valuable information for analysis.
Price index numbers measure and permit comparison of the price of certain goods;
quantity index numbers, on the other hand, measure and permit comparison of the
physical volume of goods produced or distributed or consumed.
19.2 Quantity Index Numbers
Price index numbers measure and permit comparison of the price of certain goods; quantity index
numbers, on the other hand, measure and permit comparison of the physical volume of goods
produced or distributed or consumed. Though price indices are more widely used, production indices
are highly significant as indicators of the level of output in the economy or in parts of it.
In constructing quantity index numbers, the problems confronting the statistician are analogous to
those involved in price indices. We measure changes in quantities, and when we weigh we use prices
or values as weights. Quantity indices can be obtained easily by changing p to q and q to p in the
various formulae discussed above.
Thus when Laspeyre’s method is used
∑ qp
10
Q 01 = ∑ qp × 100
00
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 243