Page 250 - DECO504_STATISTICAL_METHODS_IN_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 250
Statistical Methods in Economics
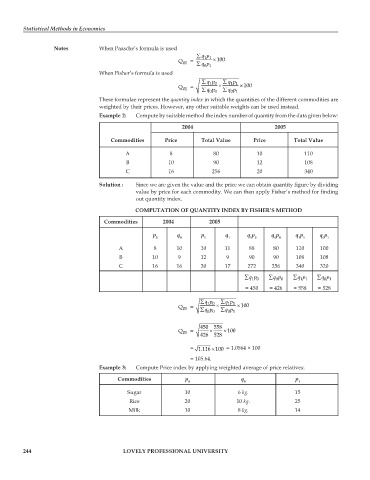
Notes When Paasche’s formula is used
∑ qp
11
Q 01 = ∑ qp × 100
01
When Fisher’s formula is used
∑ qp ∑ qp
10
11
Q 01 = ∑ qp × ∑ qp × 100
00
01
These formulae represent the quantity index in which the quantities of the different commodities are
weighted by their prices. However, any other suitable weights can be used instead.
Example 2: Compute by suitable method the index number of quantity from the data given below:
2004 2005
Commodities Price Total Value Price Total Value
A 8 80 10 110
B 10 90 12 108
C 16 256 20 340
Solution : Since we are given the value and the price we can obtain quantity figure by dividing
value by price for each commodity. We can then apply Fisher’s method for finding
out quantity index.
COMPUTATION OF QUANTITY INDEX BY FISHER’S METHOD
Commodities 2004 2005
p q p q q p q p q p q p
0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1
A 8 10 10 11 88 80 110 100
B 10 9 12 9 90 90 108 108
C 16 16 20 17 272 256 340 320
∑ qp ∑ qp ∑ qp ∑ qp
10
11
01
00
= 450 = 426 = 558 = 528
∑ qp ∑ qp
10
11
Q 01 = ∑ qp × ∑ qp × 100
01
00
450 558
Q 01 = 426 × 528 × 100
= 1.116 100× = 1.0564 × 100
= 105.64.
Example 3: Compute Price index by applying weighted average of price relatives:
Commodities p q p
0 0 1
Sugar 10 6 kg. 15
Rice 20 10 kg. 25
Milk 10 8 kg. 14
244 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY