Page 252 - DECO504_STATISTICAL_METHODS_IN_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 252
Statistical Methods in Economics
Notes
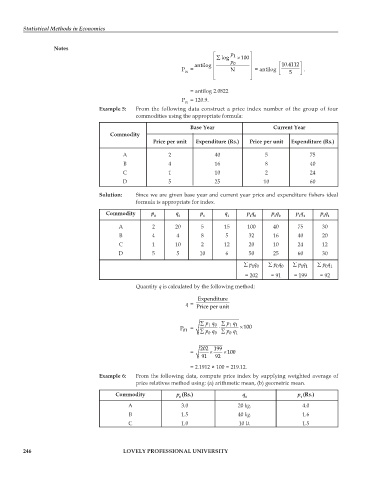
⎡ p 1 ⎤
⎢ ∑ log p × 100 ⎥
antilog ⎢ 0 ⎥ ⎡ 10.4112 ⎤
P = ⎢ N ⎥ = antilog ⎢ ⎥ .
01 ⎣ 5 ⎦
⎢ ⎣ ⎥ ⎦
= antilog 2.0822
P = 120.9.
01
Example 5: From the following data construct a price index number of the group of four
commodities using the appropriate formula:
Base Year Current Year
Commodity
Price per unit Expenditure (Rs.) Price per unit Expenditure (Rs.)
A 2 40 5 75
B 4 16 8 40
C 1 10 2 24
D 5 25 10 60
Solution: Since we are given base year and current year price and expenditure fishers ideal
formula is appropriate for index.
Commodity p q p q p q p q p q p q
0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1
A 2 20 5 15 100 40 75 30
B 4 4 8 5 32 16 40 20
C 1 10 2 12 20 10 24 12
D 5 5 10 6 50 25 60 30
∑ pq ∑ pq ∑ pq ∑ pq
00
01
10
11
= 202 = 91 = 199 = 92
Quantity q is calculated by the following method:
Expenditure
q = Price per unit
∑ 10 ∑ pq pq
11
P 01 = ∑ 0 0 ⋅ ∑ pq pq 1 × 100
0
202 199
= × × 100
91 92
= 2.1912 × 100 = 219.12.
Example 6: From the following data, compute price index by supplying weighted average of
price relatives method using: (a) arithmetic mean, (b) geometric mean.
Commodity p (Rs.) q p (Rs.)
0 0 1
A 3.0 20 kg. 4.0
B 1.5 40 kg. 1.6
C 1.0 10 lt. 1.5
246 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY