Page 39 - DECO504_STATISTICAL_METHODS_IN_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 39
Unit 3: Classification and Tabulation of Data: Frequency and Cumulative Frequency Distribution
(iii) Assuming that the age quoted (X) is the age completed on last birthday then X will be a Notes
discreate variable which can take only integral values. Hence the given distribution can
be expressed in an inclusive type classes with class interval of magnitude 7, as in the table
given below.
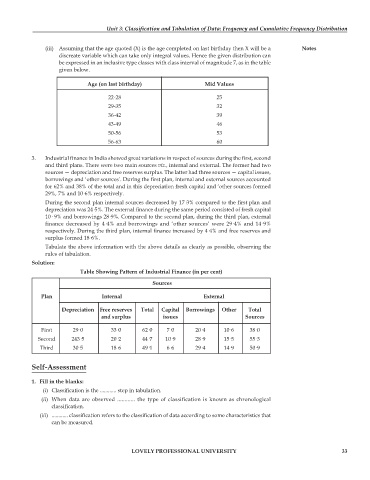
Age (on last birthday) Mid Values
22-28 25
29-35 32
36-42 39
43-49 46
50-56 53
56-63 60
3. Industrial finance in India showed great variations in respect of sources during the first, second
and third plans. There were two main sources viz., internal and external. The former had two
sources — depreciation and free reserves surplus. The latter had three sources — capital issues,
borrowings and ‘other sources’. During the first plan, internal and external sources accounted
for 62% and 38% of the total and in this depreciation fresh capital and ‘other sources formed
29%, 7% and 10·6% respectively.
During the second plan internal sources decreased by 17·3% compared to the first plan and
depreciation was 24·5%. The external finance during the same period consisted of fresh capital
10· 9% and borrowings 28·9%. Compared to the second plan, during the third plan, external
finance decreased by 4·4% and borrowings and ‘other sources’ were 29·4% and 14·9%
respectively. During the third plan, internal finance increased by 4·4% and free reserves and
surplus formed 18·6%.
Tabulate the above information with the above details as clearly as possible, observing the
rules of tabulation.
Solution:
Table Showing Pattern of Industrial Finance (in per cent)
Sources
Plan Internal External
Depreciation Free reserves Total Capital Borrowings Other Total
and surplus issues Sources
First 29·0 33·0 62·0 7·0 20·4 10·6 38·0
Second 243·5 20·2 44·7 10·9 28·9 15·5 55·3
Third 30·5 18·6 49·1 6·6 29·4 14·9 50·9
Self-Assessment
1. Fill in the blanks:
(i) Classification is the ............ step in tabulation.
(ii) When data are observed ............ the type of classification is known as chronological
classification.
(iii) ............ classification refers to the classification of data according to some characteristics that
can be measured.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 33