Page 55 - DECO504_STATISTICAL_METHODS_IN_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 55
Unit 5: Application of Mean, Median and Mode
Notes
∑ X = Sum of all the values of the variable X, i.e., X ,X ,X ,......,X .
3
1
2
N
N = Number of observations.
Steps: The formula suggests two steps in calculating mean:
(i) Add together all the values of the variable X and obtain the total ∑ X .
(ii) Divide this total by the number of observations.
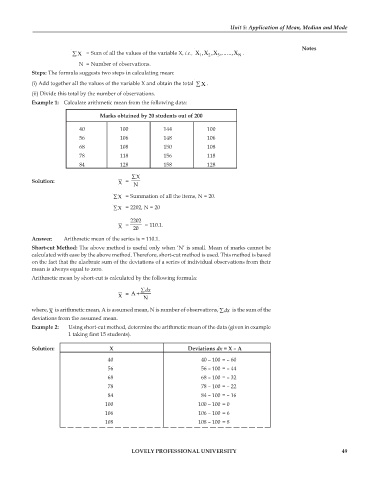
Example 1: Calculate arithmetic mean from the following data:
Marks obtained by 20 students out of 200
40 100 144 100
56 106 148 106
68 108 150 108
78 118 156 118
84 128 158 128
∑X
Solution: X = N
∑X = Summation of all the items, N = 20.
∑X = 2202, N = 20
2202
X = 20 = 110.1.
Answer: Arithmetic mean of the series is = 110.1.
Short-cut Method: The above method is useful only when ‘N’ is small. Mean of marks cannot be
calculated with ease by the above method. Therefore, short-cut method is used. This method is based
on the fact that the alzebraic sum of the deviations of a series of individual observations from their
mean is always equal to zero.
Arithmetic mean by short-cut is calculated by the following formula:
∑dx
X = A + N
where, X is arithmetic mean, A is assumed mean, N is number of observations, ∑dx is the sum of the
deviations from the assumed mean.
Example 2: Using short-cut method, determine the arithmetic mean of the data (given in example
1 taking first 15 students).
Solution: X Deviations dx = X – A
40 40 – 100 = – 60
56 56 – 100 = – 44
68 68 – 100 = – 32
78 78 – 100 = – 22
84 84 – 100 = – 16
100 100 – 100 = 0
106 106 – 100 = 6
108 108 – 100 = 8
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 49