Page 56 - DECO504_STATISTICAL_METHODS_IN_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 56
Statistical Methods in Economics
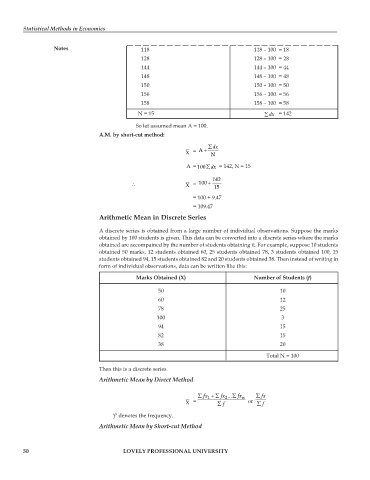
Notes 118 118 – 100 = 18
128 128 – 100 = 28
144 144 – 100 = 44
148 148 – 100 = 48
150 150 – 100 = 50
156 156 – 100 = 56
158 158 – 100 = 58
N = 15 ∑dx = 142
So let assumed mean A = 100.
A.M. by short-cut method:
∑dx
X = A + N
∑
A= 100 dx = 142, N = 15
142
∴ X = 100 + 15
= 100 + 9.47
= 109.47
Arithmetic Mean in Discrete Series
A discrete series is obtained from a large number of individual observations. Suppose the marks
obtained by 100 students is given. This data can be converted into a discrete series where the marks
obtained are accompained by the number of students obtaining it. For example, suppose 10 students
obtained 50 marks, 12 students obtained 60, 25 students obtained 78, 3 students obtained 100, 15
students obtained 94, 15 students obtained 82 and 20 students obtained 38. Then instead of writing in
form of individual observations, data can be written like this:
Marks Obtained (X) Number of Students (f)
50 10
60 12
78 25
100 3
94 15
82 15
38 20
Total N = 100
Then this is a discrete series.
Arithmetic Mean by Direct Method
∑ 1 + fx ∑ fx 2 ∑ ... fx n ∑ fx
X = ∑ f or ∑ f
'f' denotes the frequency.
Arithmetic Mean by Short-cut Method
50 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY