Page 316 - DMTH404_STATISTICS
P. 316
Statistics
Notes denotes the number of concurrences and D (= number of observations - 1) is the number of pairs
of deviation.
Note:
F 2C - DI
(i) The sign of r is taken to be equal to the sign of H D K .
C
2 C D
(ii) When is negative, we make it positive for the purpose of taking its square
D
root. However, the computed value will have a negative sign.
2 C D
(iii) The sign of r will be positive when is positive.
C
D
(iv) This method gives same weights to smaller as well as to the larger deviations.
(v) This method is suitable only for the study of short term fluctuations because it does not
take into account the changes in magnitudes of the values.
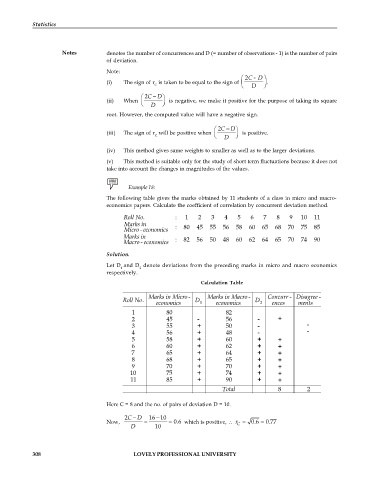
Example 18:
The following table gives the marks obtained by 11 students of a class in micro and macro-
economics papers. Calculate the coefficient of correlation by concurrent deviation method.
Roll No. : 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
Marks in
Micro - economics : 80 45 55 56 58 60 65 68 70 75 85
Marks in
Macro - economics : 82 56 50 48 60 62 64 65 70 74 90
Solution.
Let D and D denote deviations from the preceding marks in micro and macro economics
1 2
respectively.
Calculation Table
Marks in Micro - Marks in Macro - Concurr - Disagree -
Roll No. D D
economics 1 economics 2 ences ments
1 80 82
2 45 - 56 - +
3 55 + 50 - -
4 56 + 48 - -
5 58 + 60 + +
6 60 + 62 + +
7 65 + 64 + +
8 68 + 65 + +
9 70 + 70 + +
10 75 + 74 + +
11 85 + 90 + +
Total 8 2
Here C = 8 and the no. of pairs of deviation D = 10.
2 C D 16 10
Now, 0.6 which is positive, r 0.6 0.77
C
D 10
308 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY