Page 375 - DMTH504_DIFFERENTIAL_AND_INTEGRAL_EQUATION
P. 375
Differential and Integral Equation
Notes Hence (ix) with the coefficient (x) is the solution of Laplace s equation (i), which satisfy all the
given boundary conditions.
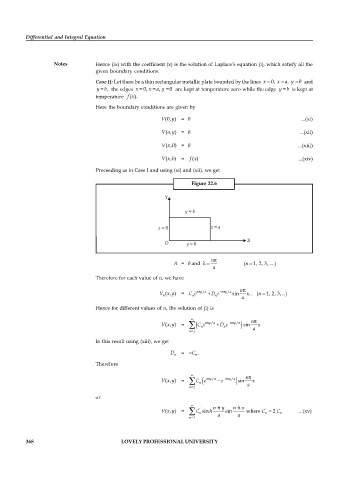
Case II: Let there be a thin rectangular metallic plate bounded by the lines x 0, x , a y 0 and
y , b the edges x 0, x , a y 0 are kept at temperature zero while the edge y b is kept at
temperature ( ).f x
Here the boundary conditions are given by
y
V (0, ) = 0 ...(xi)
y
V ( , ) = 0 ...(xii)
a
x
V ( ,0) = 0 ...(xiii)
V ( , ) = f ( ) ...(xiv)
b
x
x
Proceeding as in Case I and using (xi) and (xii), we get
Figure 22.6
n
A = 0 and (n 1, 2, 3, ....)
a
Therefore for each value of n, we have
n
/a
n y
n y
/a
V ( , ) = C e D e sin x ... (n 1, 2, 3,...)
y
x
n n n
a
Hence for different values of n, the solution of (i) is
n
x
V ( , ) = C e n y /a D e n y /a sin x
y
n
n
n 1 a
In this result using (xiii), we get
D n = C n .
Therefore
n
n y
/a
n y
/a
y
x
V ( , ) = C e e sin x
n
n 1 a
or
n y n x
V ( , ) = C n sinh sin where C n 2 C ...(xv)
y
x
n
n 1 a a
368 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY