Page 189 - DCOM202_COST_ACCOUNTING_I
P. 189
Unit 9: Absorption of Overheads
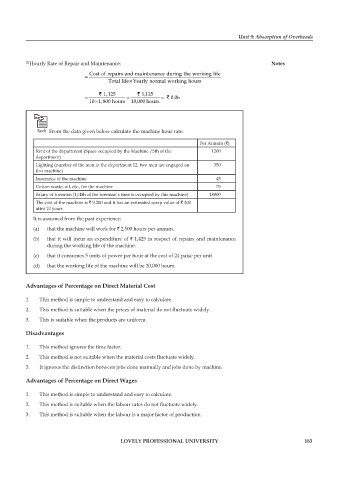
(2) Hourly Rate of Repair and Maintenance: Notes
Cost of repairsand ma int enance during theworking life
=
×
Tottal lifeYearlynormalworking hours
` 1 125 ` 1,125
,
.
= = = ` 006
,
10 ×1 800 hours 18,000 hours
Task From the data given below calculate the machine hour rate:
per Annum (`)
Rent of the department (Space occupied by the Machine /5th of the 1200
department)
Lighting (number of the men in the department 12, two men are engaged on 350
this machine)
Insurance of the machine 45
Cotton waste, oil, etc., for the machine 75
Salary of foreman (1/4th of the foreman’s time is occupied by this machine) 18000
The cost of the machine is ` 9,200 and it has an estimated scrap value of ` 200
after 10 years
It is assumed from the past experience:
(a) that the machine will work for ` 2,500 hours per annum.
(b) that it will incur an expenditure of ` 1,425 in respect of repairs and maintenance
during the working life of the machine.
(c) that it consumes 5 units of power per hour at the cost of 24 paise per unit.
(d) that the working life of the machine will be 20,000 hours.
Advantages of Percentage on direct Material Cost
1. This method is simple to understand and easy to calculate.
2. This method is suitable when the prices of material do not fluctuate widely.
3. This is suitable when the products are uniform.
disadvantages
1. This method ignores the time factor.
2. This method is not suitable when the material costs fluctuate widely.
3. It ignores the distinction between jobs done manually and jobs done by machine.
Advantages of Percentage on direct Wages
1. This method is simple to understand and easy to calculate.
2. This method is suitable when the labour rates do not fluctuate widely.
3. This method is suitable when the labour is a major factor of production.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 183