Page 184 - DCOM202_COST_ACCOUNTING_I
P. 184
Cost Accounting – I
Notes 3. Time factor: Overhead rate should have some relation to the time taken by various
jobs for completion. Thus, if a job takes twice as much another job, the first job should
be charged twice the amount charged to the second job. It is because of this reason
that direct wages percentage rate is preferred over direct material cost percentage
rate.
4. Manual or machine work: The work done by manual labour is to be distinguished
from work done by machines and different overhead rates should be applied for
manual and machine work.
5. Different overhead rates: Different overhead rates should be ascertained for different
departments where the nature of work done by one department is different from the
work done by other department or departments.
6. Information: The selection of most appropriate overhead rate depends on the extent
of information available or recorded.
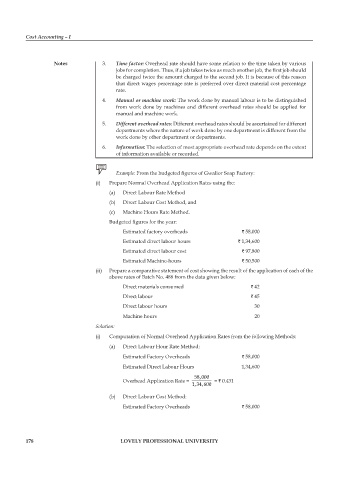
Example: From the budgeted figures of Gwalior Soap Factory:
(i) prepare Normal Overhead Application Rates using the:
(a) Direct Labour Rate Method
(b) Direct Labour Cost Method, and
(c) Machine Hours Rate Method.
Budgeted figures for the year:
Estimated factory overheads ` 58,000
Estimated direct labour hours ` 1,34,600
Estimated direct labour cost ` 97,800
Estimated Machine-hours ` 50,500
(ii) prepare a comparative statement of cost showing the result of the application of each of the
above rates of Batch No. 488 from the data given below:
Direct materials consumed ` 42
Direct labour ` 45
Direct labour hours 30
Machine hours 20
Solution:
(i) Computation of Normal Overhead Application Rates from the following Methods:
(a) Direct Labour Hour Rate Method:
Estimated Factory Overheads ` 58,000
Estimated Direct Labour Hours 1,34,600
,
58 000
Overhead Application Rate = = ` 0.431
,
134 600
,
(b) Direct Labour Cost Method:
Estimated Factory Overheads ` 58,000
178 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY