Page 140 - DCOM205_ACCOUNTING_FOR_COMPANIES_II
P. 140
Unit 7: Accounting for Banking Companies
notes
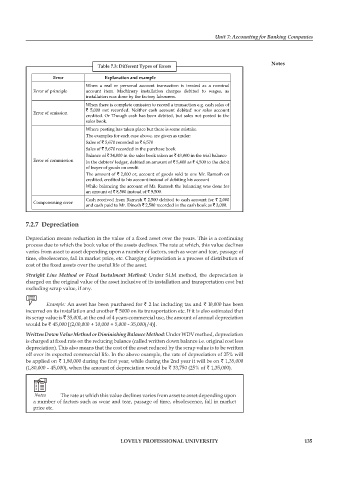
table 7.3: Different types of errors
error explanation and example
When a real or personal account transaction is treated as a nominal
Error of principle account item. Machinery installation charges debited to wages, as
installation was done by the factory labourers.
When there is complete omission to record a transaction e.g. cash sales of
` 5,000 not recorded. Neither cash account debited nor sales account
Error of omission credited. Or Though cash has been debited, but sales not posted to the
sales book.
Where posting has taken place but there is some mistake.
The examples for each case above, are given as under:
Sales of ` 5,670 recorded as ` 6,570
Sales of ` 5,670 recorded in the purchase book
Balance of ` 34,000 in the sales book taken as ` 43,000 in the trial balance
Error of commission In the debtors' ledger, debited an amount of ` 5,400 as ` 4,500 to the debit
of buyer of goods on credit
The amount of ` 2,000 or, account of goods sold to one Mr. Ramesh on
credited, credited to his account instead of debiting his account
While balancing the account of Mr. Ramesh the balancing was done for
an amount of ` 8,500 instead of ` 9,500.
Cash received from Ramesh ` 2,500 debited to cash account for ` 2,000
Compensating error and cash paid to Mr. Dinesh ` 2,500 recorded in the cash book as ` 3,000.
7.2.7 Depreciation
Depreciation means reduction in the value of a fixed asset over the years. This is a continuing
process due to which the book value of the assets declines. The rate at which, this value declines
varies from asset to asset depending upon a number of factors, such as wear and tear, passage of
time, obsolescence, fall in market price, etc. Charging depreciation is a process of distribution of
cost of the fixed assets over the useful life of the asset.
Straight Line Method or Fixed Instalment Method: Under SLM method, the depreciation is
charged on the original value of the asset inclusive of its installation and transportation cost but
excluding scrap value, if any.
Example: An asset has been purchased for ` 2 lac including tax and ` l0,000 has been
incurred on its installation and another ` 5000 on its transportation etc. If it is also estimated that
its scrap value is ` 35,000, at the end of 4 years commercial use, the amount of annual depreciation
would be ` 45,000 [(2,00,000 + 10,000 + 5,000 - 35,000)/4)].
Written Down Value Method or Diminishing Balance Method: Under WDV method, depreciation
is charged at fixed rate on the reducing balance (called written down balance i.e. original cost less
depreciation). This also means that the cost of the asset reduced by the scrap value is to be written
off over its expected commercial life. In the above example, the rate of depreciation of 25% will
be applied on ` 1,80,000 during the first year, while during the 2nd year it will be on ` 1,35,000
(1,80,000 – 45,000), when the amount of depreciation would be ` 33,750 (25% of ` 1,35,000).
Notes The rate at which this value declines varies from asset to asset depending upon
a number of factors such as wear and tear, passage of time, obsolescence, fall in market
price etc.
lovely professional university 135