Page 141 - DCOM205_ACCOUNTING_FOR_COMPANIES_II
P. 141
Accounting for Companies – II
notes 7.2.8 Bank reconciliation
Reconciliation is a statement with the help of which a party reconciles its cashbook with the bank
pass book based on certain causes of difference between these two books.
procedure for reconciliation
Whenever the task of reconciliation is taken in hand, the following procedure can be
adopted:
1. Make comparison of two books i.e. cash book and passbook to locate the transactions which
appear in one of books and not the other.
2. Take balance of one book as starting point, say balance as per cash book or pass book. This
balance can be credit balance or debit balance. This gives rise to four situations (debit or
credit balance as per cash book or as per passbook).
3. Adjust the balance with starting point by adding the amount of transaction or deducting the
amount of transaction depending upon the nature of the transaction.
4. The opposite balance at the end of these adjustments will be answer (if balance is credit in
cash book, it will be debit in pass book and vice versa).
Adjustment entries: After competition of the process of trial balancing or drawing final accounts,
at times, subsequently, it may come to the notice of the management that certain expenses which
were to be incurred have not been paid and certain expenses have been paid in advance. Similarly,
there may be some income which was due to be received, but has been received so far and some
income which was still not due has been received. As a result, the actual position of profit or loss
may not be reflected unless these are adjusted in the final accounts. The summary of some of the
adjustments is given as under Table 7.4 and 7.5.
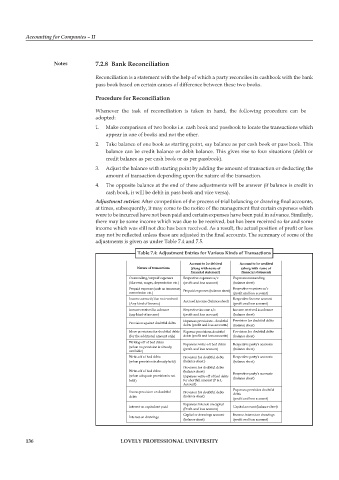
table 7.4: adjustment entries for various kinds of transactions
account to be debited account to be credited
nature of transactions (along with name of (along with name of
financial statement) financial statement)
Outstanding/unpaid expenses Respective expenses a/c Expenses outstanding
(like rent, wages, depreciation etc.) (profit and loss account) (balance sheet)
Prepaid expense (such as insurance, Respective expenses a/c
commission etc.) Prepaid expenses (balance sheet) (profit and loss account)
Income accrued/due not received Accrued income (balance sheet) Respective Income account
(Any kind of Income) (profit and loss account)
Income received In advance Respective income a/c Income received in advance
(any kind of income) (profit and loss account) (balance sheet)
Provision against doubtful debts Expenses provisions - doubtful Provision for doubtful debts
debts (profit and loss accounts) (balance sheet)
More provisions for doubtful debts Expense provisions-doubtful Provision for doubtful debts
(for the additional amount only) debts (profit and loss accounts) (balance sheet)
Writing-off of bad debts Expenses: write-off bad debts Respective party's accounts
(when no provision is already
available) (profit and loss account) (balance sheet)
Write-off of bad debts Provision for doubtful debts Respective party's accounts
(when provision is already held) (balance sheet ) (balance sheet)
Provision for doubtful debts
Write-off of bad debts (balance sheet) Respective party's accounts
(when adequate provision is not Expenses write-off of bad debts (balance sheet)
held) for shortfall amount (P & L
Account)
Expenses provision doubtful
Excess provision on doubtful Provision for doubtful debts debts
debts (balance sheet)
(profit and loss account)
Expenses: Interest on capital
Interest on capital not paid Capital account (balance sheet)
(Profit and loss account)
Capital or drawings account Income-interest on drawings
Interest on drawings
(balance sheet) (profit and loss account)
136 lovely professional university