Page 227 - DCOM206_COST_ACCOUNTING_II
P. 227
Cost Accounting – II
Notes If the standard cost is more than the actual cost, the variance will be favourable and on the
other hand, if the actual cost is more than the standard cost, the variance will be adverse or
be unfavourable.
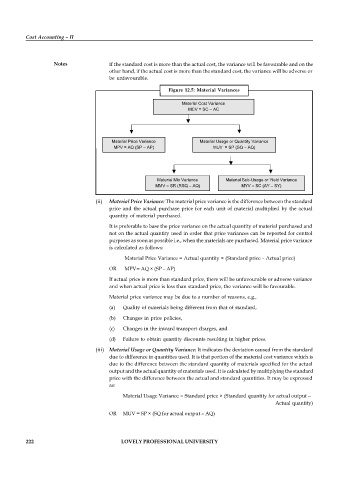
Figure 12.5: Material Variances
Material Cost Variance
MCV = SC – AC
Material Price Variance Material Usage or Quantity Variance
MPV = AQ (SP – AP) MUV = SP (SQ – AQ)
Material Mix Variance Material Sub-Usage or Yield Variance
MMV = SR (RSQ – AQ) MYV = SC (AY – SY)
(ii) Material Price Variance: The material price variance is the difference between the standard
price and the actual purchase price for each unit of material multiplied by the actual
quantity of material purchased.
It is preferable to base the price variance on the actual quantity of material purchased and
not on the actual quantity used in order that price variances can be reported for control
purposes as soon as possible i.e., when the materials are purchased. Material price variance
is calculated as follows:
Material Price Variance = Actual quantity × (Standard price – Actual price)
OR MPV= AQ × (SP – AP)
If actual price is more than standard price, there will be unfavourable or adverse variance
and when actual price is less than standard price, the variance will be favourable.
Material price variance may be due to a number of reasons, e.g.,
(a) Quality of materials being different from that of standard,
(b) Changes in price policies,
(c) Changes in the inward transport charges, and
(d) Failure to obtain quantity discounts resulting in higher prices.
(iii) Material Usage or Quantity Variance: It indicates the deviation caused from the standard
due to difference in quantities used. It is that portion of the material cost variance which is
due to the difference between the standard quantity of materials specified for the actual
output and the actual quantity of materials used. It is calculated by multiplying the standard
price with the difference between the actual and standard quantities. It may be expressed
as:
Material Usage Variance = Standard price × (Standard quantity for actual output –
Actual quantity)
OR MUV = SP × (SQ for actual output – AQ)
222 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY