Page 231 - DCOM206_COST_ACCOUNTING_II
P. 231
Cost Accounting – II
Notes If the actual labour cost is lower than the standard labour cost, the variance is favourable.
On the other hand, if the actual labour cost is higher than the standard labour cost, the
variance will be adverse.
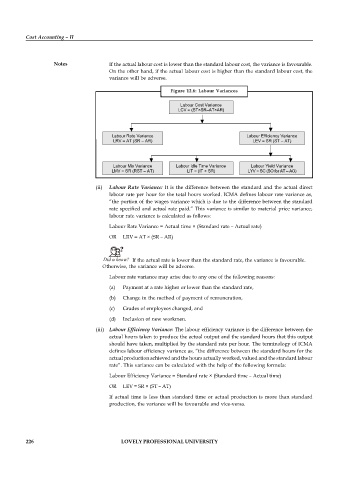
Figure 12.6: Labour Variances
Labour Cost Variance
LCV = (ST×SR–AT×AR)
Labour Rate Variance Labour Efficiency Variance
LRV = AT (SR – AR) LEV = SR (ST – AT)
Labour Mix Variance Labour Idle Time Variance Labour Yield Variance
LMV = SR (RST – AT) LIT = (IT × SR) LYV = SC (SO for AT – AO)
(ii) Labour Rate Variance: It is the difference between the standard and the actual direct
labour rate per hour for the total hours worked. ICMA defines labour rate variance as,
“the portion of the wages variance which is due to the difference between the standard
rate specified and actual rate paid.” This variance is similar to material price variance;
labour rate variance is calculated as follows:
Labour Rate Variance = Actual time × (Standard rate – Actual rate)
OR LRV = AT × (SR – AR)
Did u know? If the actual rate is lower than the standard rate, the variance is favourable.
Otherwise, the variance will be adverse.
Labour rate variance may arise due to any one of the following reasons:
(a) Payment at a rate higher or lower than the standard rate,
(b) Change in the method of payment of remuneration,
(c) Grades of employees changed, and
(d) Inclusion of new workmen.
(iii) Labour Efficiency Variance: The labour efficiency variance is the difference between the
actual hours taken to produce the actual output and the standard hours that this output
should have taken, multiplied by the standard rate per hour. The terminology of ICMA
defines labour efficiency variance as, “the difference between the standard hours for the
actual production achieved and the hours actually worked, valued and the standard labour
rate”. This variance can be calculated with the help of the following formula:
Labour Efficiency Variance = Standard rate × (Standard time – Actual time)
OR LEV = SR × (ST – AT)
If actual time is less than standard time or actual production is more than standard
production, the variance will be favourable and vice-versa.
226 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY