Page 187 - DECO405_MANAGERIAL_ECONOMICS
P. 187
Managerial Economics
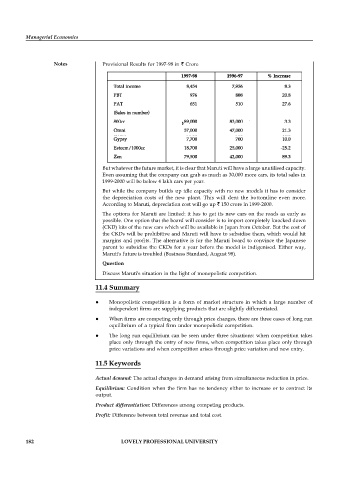
Notes Provisional Results for 1997-98 in Crore
1
But whatever the future market, it is clear that Maruti will have a large unutilised capacity.
Even assuming that the company can grab as much as 30,000 more cars, its total sales in
1999-2000 will be below 4 lakh cars per year.
But while the company builds up idle capacity with no new models it has to consider
the depreciation costs of the new plant. This will dent the bottomline even more.
According to Maruti, depreciation cost will go up 150 crore in 1999-2000.
The options for Maruti are limited: it has to get its new cars on the roads as early as
possible. One option that the board will consider is to import completely knocked down
(CKD) kits of the new cars which will be available in Japan from October. But the cost of
the CKDs will be prohibitive and Maruti will have to subsidise them, which would hit
margins and profits. The alternative is for the Maruti board to convince the Japanese
parent to subsidise the CKDs for a year before the model is indigenised. Either way,
Maruti's future is troubled (Business Standard, August 98).
Question
Discuss Maruti's situation in the light of monopolistic competition.
11.4 Summary
Monopolistic competition is a form of market structure in which a large number of
independent firms are supplying products that are slightly differentiated.
When firms are competing only through price changes, there are three cases of long run
equilibrium of a typical firm under monopolistic competition.
The long run equilibrium can be seen under three situations: when competition takes
place only through the entry of new firms, when competition takes place only through
price variations and when competition arises through price variation and new entry.
11.5 Keywords
Actual demand: The actual changes in demand arising from simultaneous reduction in price.
Equilibrium: Condition when the firm has no tendency either to increase or to contract its
output.
Product differentiation: Differences among competing products.
Profit: Difference between total revenue and total cost.
182 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY