Page 192 - DMGT405_FINANCIAL%20MANAGEMENT
P. 192
Financial Management
Notes In brief, this method can at best be considered as a crude method of incorporating risk into the
capital budgeting analysis.
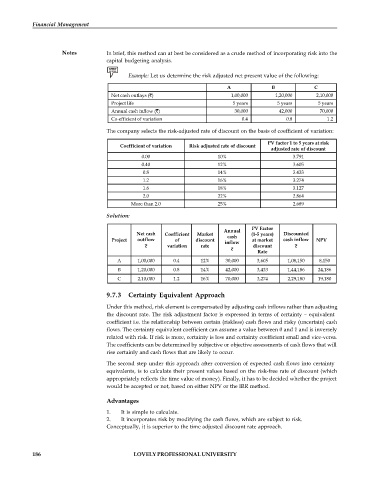
Example: Let us determine the risk adjusted net present value of the following:
A B C
Net cash outlays ( ) 1,00,000 1,20,000 2,10,000
Project life 5 years 5 years 5 years
Annual cash inflow ( ) 30,000 42,000 70,000
Co-efficient of variation 0.4 0.8 1.2
The company selects the risk-adjusted rate of discount on the basis of coefficient of variation:
PV factor 1 to 5 years at risk
Coefficient of variation Risk adjusted rate of discount
adjusted rate of discount
0.00 10% 3.791
0.40 12% 3.605
0.8 14% 3.433
1.2 16% 3.274
1.6 18% 3.127
2.0 22% 2.864
More than 2.0 25% 2.689
Solution:
PV Factor
Annual
Net cash Coefficient Market cash (1-5 years) Discounted
Project outflow of discount inflow at market cash inflow NPV
variation rate discount
Rate
A 1,00,000 0.4 12% 30,000 3,605 1,08,150 8,150
B 1,20,000 0.8 14% 42,000 3,433 1,44,186 24,186
C 2,10,000 1.2 16% 70,000 3,274 2,29,180 19,180
9.7.3 Certainty Equivalent Approach
Under this method, risk element is compensated by adjusting cash inflows rather than adjusting
the discount rate. The risk adjustment factor is expressed in terms of certainty – equivalent
coefficient i.e. the relationship between certain (riskless) cash flows and risky (uncertain) cash
flows. The certainty equivalent coefficient can assume a value between 0 and 1 and is inversely
related with risk. If risk is more, certainty is less and certainty coefficient small and vice-versa.
The coefficients can be determined by subjective or objective assessments of cash flows that will
rise certainly and cash flows that are likely to occur.
The second step under this approach after conversion of expected cash flows into certainty
equivalents, is to calculate their present values based on the risk-free rate of discount (which
appropriately reflects the time value of money). Finally, it has to be decided whether the project
would be accepted or not, based on either NPV or the IRR method.
Advantages
1. It is simple to calculate.
2. It incorporates risk by modifying the cash flows, which are subject to risk.
Conceptually, it is superior to the time adjusted discount rate approach.
186 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY