Page 291 - DMGT405_FINANCIAL%20MANAGEMENT
P. 291
Unit 13: Management of Cash
Notes
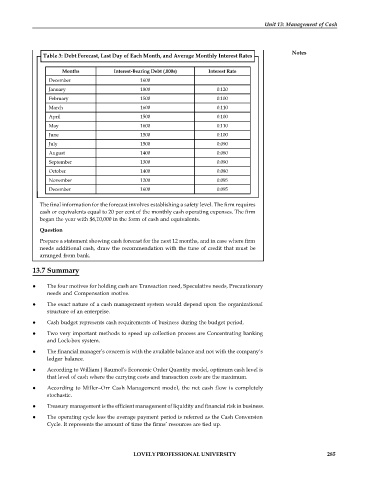
Table 3: Debt Forecast, Last Day of Each Month, and Average Monthly Interest Rates
Months Interest-Bearing Debt (,000s) Interest Rate
December 1600
January 1800 0.120
February 1500 0.100
March 1600 0.110
April 1500 0.100
May 1600 0.110
June 1500 0.100
July 1500 0.090
August 1400 0.080
September 1300 0.090
October 1400 0.080
November 1200 0.095
December 1600 0.095
The final information for the forecast involves establishing a safety level. The firm requires
cash or equivalents equal to 20 per cent of the monthly cash operating expenses. The firm
began the year with $6,10,000 in the form of cash and equivalents.
Question
Prepare a statement showing cash forecast for the next 12 months, and in case where firm
needs additional cash, draw the recommendation with the tune of credit that must be
arranged from bank.
13.7 Summary
The four motives for holding cash are Transaction need, Speculative needs, Precautionary
needs and Compensation motive.
The exact nature of a cash management system would depend upon the organizational
structure of an enterprise.
Cash budget represents cash requirements of business during the budget period.
Two very important methods to speed up collection process are Concentrating banking
and Lock-box system.
The financial manager’s concern is with the available balance and not with the company’s
ledger balance.
According to William J Baumol’s Economic Order Quantity model, optimum cash level is
that level of cash where the carrying costs and transaction costs are the maximum.
According to Miller–Orr Cash Management model, the net cash flow is completely
stochastic.
Treasury management is the efficient management of liquidity and financial risk in business.
The operating cycle less the average payment period is referred as the Cash Conversion
Cycle. It represents the amount of time the firms’ resources are tied up.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 285