Page 89 - DCOM510_FINANCIAL_DERIVATIVES
P. 89
Financial Derivatives
Notes increase as volatility increases. The buyer of the option receives full benefit of favourable
outcomes but avoids the unfavourable ones (option price value has zero value).
4. Risk free Interest Rates: The risk-free interest rate is the interest rate that may be obtained
in the marketplace with virtually no risk. The affect of the risk-free interest rate is less
clear-cut. It is found that put option prices decline as the risk-free rate increases whereas
the prices of calls always increase as the risk-free interest rate increases. The higher the
interest rate, the lower the present value of the exercise price. As a result, the value of the
call will increase. The opposite is true for puts. The decrease in the present value of the
exercise price will adversely affect the price of the put option. All other factors remaining
constant, the higher the interest rate the greater the cost of buying the underlying asset
and carrying it to the expiration date of the call option. Hence, the higher the short risk
free interest rate, the greater the price of a call option.
5. Cash Dividends: Dividends have the effect of reducing the stock price on the ex-dividend
date. This has a negative effect on the value of call options and a positive effect on the
value of put options. When dividends are announced then the stock prices on ex-dividend
are reduced. This is favourable for the put option and unfavourable for the call option. On
ex-dividend dates, the stock price will fall by the amount of the dividend. So, the higher
the dividends, the lower the value of a call relative to the stock. This effect will work in the
opposite direction for puts. As more dividends are paid out, the stock price will jump
down on the ex-date which is exactly what you are looking for with a put.
6. Time to Expiration: Generally, both calls and puts will benefit from increased time to
expiration. The reason is that there is more time for a big move in the stock price. Consider
the case of two options that differ only as far as their expiration date is concerned. The
owner of the long-life option has all the exercise opportunities open to the owner of the
short-life option and more. The long-life option must therefore always be worth at least as
much as the short life option. As the time to expiration increases, the present value of the
exercise price decreases. This will increase the value of the call and decrease the value of
the put. Also, as the time to expiration increases, there is a greater amount of time for the
stock price to be reduced by a cash dividend.
Notes This reduces the call value but increases the put value.
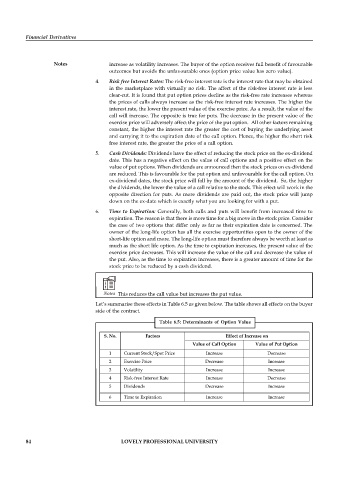
Let’s summarise these effects in Table 6.5 as given below. The table shows all effects on the buyer
side of the contract.
Table 6.5: Determinants of Option Value
S. No. Factors Effect of Increase on
Value of Call Option Value of Put Option
1 Current Stock/Spot Price Increase Decrease
2 Exercise Price Decrease Increase
3 Volatility Increase Increase
4 Risk-free Interest Rate Increase Decrease
5 Dividends Decrease Increase
6 Time to Expiration Increase Increase
84 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY