Page 111 - DCAP108_DIGITAL_CIRCUITS_AND_LOGIC_DESIGNS
P. 111
Digital Circuits and Logic Design
Notes Introduction
An integrated circuit, commonly referred to as an IC, is a microscopic array of electronic circuits
and components that has been diffused or implanted onto the surface of a single crystal, or chip, of
semiconducting material such as silicon. It is called an integrated circuit because the components,
circuits, and base material are all made together, or integrated, out of a single piece of silicon,
as opposed to a discrete circuit in which the components are made separately from different
materials and assembled later. ICs range in complexity from simple logic modules and amplifiers
to complete microcomputers containing millions of elements.
The impact of integrated circuits on our lives has been enormous. ICs have become the principal
components of almost all electronic devices. These miniature circuits have demonstrated low
cost, high reliability, low power requirements, and high processing speeds compared to the
vacuum tubes and transistors which preceded them. Integrated circuit microcomputers are now
used as controllers in equipment such as machine tools, vehicle operating systems, and other
applications where hydraulic, pneumatic, or mechanical controls were previously used. Because
IC microcomputers are smaller and more versatile than previous control mechanisms, they allow
the equipment to respond to a wider range of input and produce a wider range of output. They
can also be reprogrammed without having to redesign the control circuitry. Integrated circuit
microcomputers are so inexpensive that they are even found in children’s electronic toys.
The first integrated circuits were created in the late 1950s in response to a demand from the
military for miniaturized electronics to be used in missile control systems. At the time, transistors
and printed circuit boards were the state-of-the-art electronic technology. Although transistors
made many new electronic applications possible, engineers were still unable to make a small
enough package for the large number of components and circuits required in complex devices
like sophisticated control systems and hand-held programmable calculators. Several companies
were in competition to produce a breakthrough in miniaturized electronics, and their development
efforts were so close that there is some question as to which company actually produced the first
IC. In fact, when the integrated circuit was finally patented in 1959, the patent was awarded jointly
to two individuals working separately at two different companies.
7.1 Resistor-Transistor Logic (RTL)
Resistor-Transistor Logic, or RTL, refers to the obsolete technology for designing and fabricating
digital circuits that employ logic gates consisting of nothing but transistors and resistors. RTL
gates are now seldom used, if at all, in modern digital electronics design because it has several
drawbacks, such as bulkiness, low speed, limited fan-out, and poor noise margin. A basic
understanding of what RTL is, however, would be helpful to any engineer who wishes to get
familiarized with TTL, which for the past many years has become widely used in digital devices
such as logic gates, latches, gates, counters, and the like.
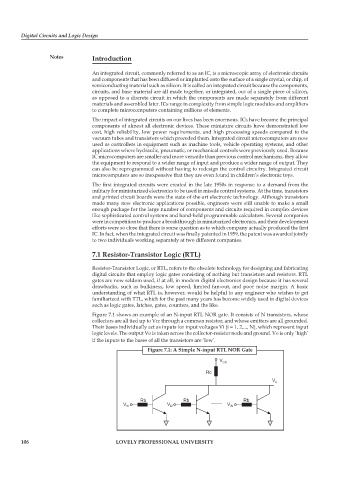
Figure 7.1 shows an example of an N-input RTL NOR gate. It consists of N transistors, whose
collectors are all tied up to Vcc through a common resistor, and whose emitters are all grounded.
Their bases individually act as inputs for input voltages Vi (i = 1, 2,..., N), which represent input
logic levels. The output Vo is taken across the collector-resistor node and ground. Vo is only ‘high’
if the inputs to the bases of all the transistors are ‘low’.
Figure 7.1: A Simple N-input RTL NOR Gate
106 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY