Page 243 - DCAP108_DIGITAL_CIRCUITS_AND_LOGIC_DESIGNS
P. 243
Digital Circuits and Logic Design
Notes Probably the most important single reason for investigating other methods of conversion is to
determine ways to reduce the conversion time. Recall that the simultaneous converter has a
very fast conversion time. The counter converter is simple logically but has a relatively long
conversion time. The continuous converter has a very fast conversion time once it is locked
on the signal but loses this advantage when multiplexing inputs.
12.8.1 Successive Approximation
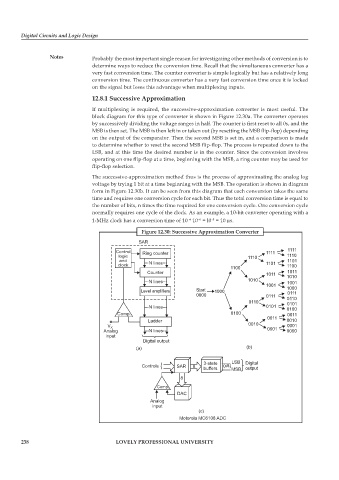
If multiplexing is required, the successive-approximation converter is most useful. The
block diagram for this type of converter is shown in Figure 12.30a. The converter operates
by successively dividing the voltage ranges in half. The counter is first reset to all 0s, and the
MSB is then set. The MSB is then left in or taken out (by resetting the MSB flip-flop) depending
on the output of the comparator. Then the second MSB is set in, and a comparison is made
to determine whether to reset the second MSB flip-flop. The process is repeated down to the
LSB, and at this time the desired number is in the counter. Since the conversion involves
operating on one flip-flop at a time, beginning with the MSB, a ring counter may be used for
flip-flop selection.
The successive-approximation method thus is the process of approximating the analog log
voltage by trying 1 bit at a time beginning with the MSB. The operation is shown in diagram
form in Figure 12.30b. It can be seen from this diagram that each conversion takes the same
time and requires one conversion cycle for each bit. Thus the total conversion time is equal to
the number of bits, n times the time required for one conversion cycle. One conversion cycle
normally requires one cycle of the clock. As an example, a 10-bit converter operating with a
1-MHz clock has a conversion time of 10 * 10 = l0 = 10 µs.
–6
–5
Figure 12.30: Successive Approximation Converter
SAR
1111
Control Ring counter 1111
logic 1110 1110
and 1101
clock N lines 1101 1100
1100
1011
Counter 1011 1010
N lines 1010 1001
1001
Level amplifiers Start 1000 1000
0000 0111 0111
0110
0110 0101
N lines 0101
0100
Comp. 0100 0011
0011
Ladder 0010
V X 0010 0001
Analog N lines 0001 0000
input
Digital output
b
a
() ()
3-state LSB Digital
Controls SAR 8 (x8)
buffers MSB output
8
Comp.
DAC
Analog
input
c
()
Motorola MC6108 ADC
238 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY