Page 85 - DCAP108_DIGITAL_CIRCUITS_AND_LOGIC_DESIGNS
P. 85
Digital Circuits and Logic Design
Notes
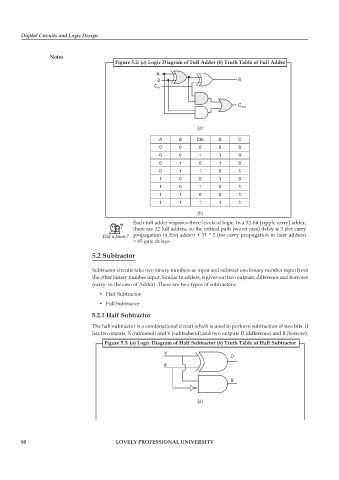
Figure 5.2: (a) Logic Diagram of Full Adder (b) Truth Table of Full Adder
(a)
A B Cin S C
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 1 1 0
0 1 0 1 0
0 1 1 0 1
1 0 0 1 0
1 0 1 0 1
1 1 0 0 1
1 1 1 1 1
(b)
Each full adder requires three levels of logic. In a 32-bit [ripple carry] adder,
there are 32 full adders, so the critical path (worst case) delay is 3 (for carry
propagation in first adder) + 31 * 2 (for carry propagation in later adders)
= 65 gate delays.
5.2 Subtractor
Subtractor circuits take two binary numbers as input and subtract one binary number input from
the other binary number input. Similar to adders, it gives out two outputs, difference and borrows
(carry–in the case of Adder). There are two types of subtractors:
• Half Subtractor
• Full Subtractor
5.2.1 Half Subtractor
The half-subtractor is a combinational circuit which is used to perform subtraction of two bits. It
has two inputs, X (minuend) and Y (subtrahend) and two outputs D (difference) and B (borrow).
Figure 5.3: (a) Logic Diagram of Half Subtractor (b) Truth Table of Half Subtractor
(a)
80 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY